| CPC C23C 16/45536 (2013.01) [C23C 16/06 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
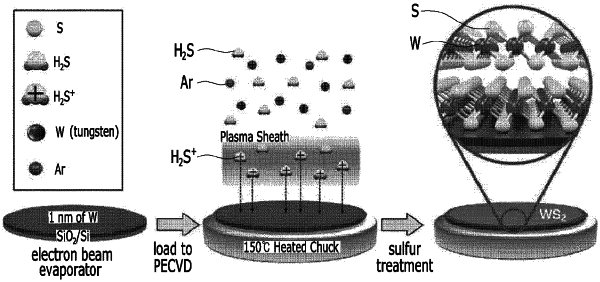
1. A method of producing an octahedral transition metal dichalcogenide, comprising:
forming a transition metal layer on a substrate; and
injecting a chalcogenide-containing gas onto the substrate together with a plasma treatment,
wherein the transition metal layer comprises a member selected from the group consisting of W, Cu, Ni, Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Zn, Y, Zr, Nb, Tc, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Cd, Hf, Ta, Re, Os, Ir, Pt, Au, Hg, Rf, Db, Sg, Bh, Hs, Mt, Ds, Rg, Cn, and combinations thereof;
the chalcogenide-containing gas is supplied at 10 sccm to 30 sccm; and
the injecting of the chalcogenide-containing gas is performed at a temperature in a range of 100° C. to 200° C., and
wherein the chalcogenide-containing gas forms argon ions (Ar+) and hydrogen sulfide ions (H2S+) during the plasma treatment.
|