| CPC B01J 20/267 (2013.01) [B01D 53/226 (2013.01); B01D 53/229 (2013.01); B01D 53/62 (2013.01); B01D 53/81 (2013.01); B01J 20/28007 (2013.01); B01J 20/28011 (2013.01); B01J 20/28047 (2013.01); B01J 20/28061 (2013.01); B01J 20/28064 (2013.01); B01J 20/3085 (2013.01); B01J 20/3208 (2013.01); B01J 20/3217 (2013.01); B01J 20/3268 (2013.01); B01D 2253/202 (2013.01); B01D 2253/25 (2013.01); B01D 2253/304 (2013.01); B01D 2253/306 (2013.01); B01D 2253/342 (2013.01); B01D 2257/504 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
1. A method for carbon dioxide (CO2) sequestration, comprising:
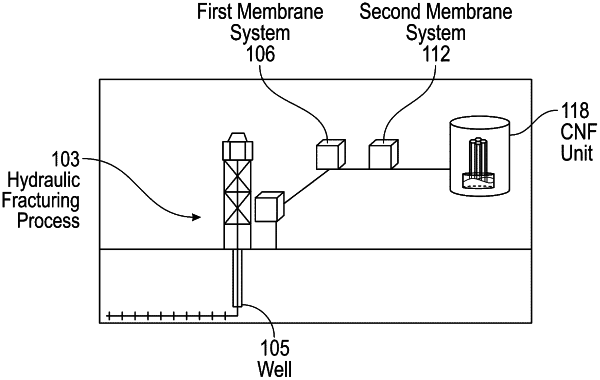
locating a CO2 producing process, wherein the CO2 producing process produces a feed stream;
separating, using a first membrane system, the feed stream into a mixed solid and liquid stream and a first gas stream;
separating, using a second membrane system, the first gas stream to produce a second gas stream and a CO2 rich stream comprising CO2;
directing the CO2 rich stream to a cellulose nanofiber (CNF) aerogel unit, comprising,
a CNF aerogel, comprising a monolithic structure, wherein the monolithic structure comprises;
an aerogel matrix,
a plurality of crosslinked CNFs, and
a plurality of cellulose nanocrystal acetone (a-CNC) suspension particles,
wherein the plurality of crosslinked CNFs and the plurality of a-CNC suspension particles are dispersed throughout the aerogel matrix; and
adsorbing, using the CNF aerogel unit, the CO2 from the CO2 rich stream.
|