| CPC A61M 5/1723 (2013.01) [G16H 10/60 (2018.01); G16H 20/17 (2018.01); G16H 40/40 (2018.01); G16H 40/67 (2018.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01); G16H 70/40 (2018.01); A61M 2005/14208 (2013.01); A61M 2230/201 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
1. A system for the delivery of a glucose altering substance to a patient, the system comprising:
a glucose sensor configured to provide a sensor glucose measurement signal representative of a real time glucose concentration;
an insulin delivery device configured to deliver insulin to a patient in response to control signals; and
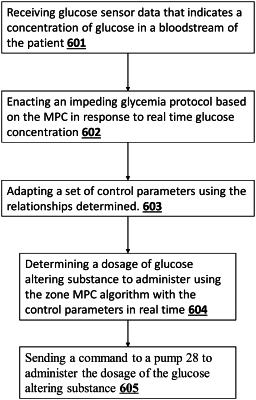
a controller programmed to receive the sensor glucose measurement signal from the glucose sensor, wherein the sensor glucose measurement signal received indicates a concentration of the real time glucose concentration in a bloodstream,
wherein the controller is further configured to enact an impeding glycemia protocol based on a zone model predictive control (MPC) algorithm in response to the real time glucose concentration, wherein the impeding glycemia protocol comprises determining a relationship between predicted glucose concentrations, a rate of change of the predicted glucose concentrations, and a set of control parameters that determine insulin doses above and below a patient-specific basal rate; wherein the set of control parameters comprise control input glucose velocity penalties; and wherein the control input glucose velocity penalties comprise separate sets of control input glucose velocity penalties for hyperlycemia and hypoglycemia;
wherein the controller is further configured to adapt the set of control parameters using the relationship determined,
determine a dosage of the glucose altering substance to administer, using the zone MPC algorithm with the control parameters, in real time, and
send a command to the insulin delivery device to administer the dosage of the glucose altering substance.
|