| CPC A01G 31/02 (2013.01) [A01G 9/241 (2013.01); A01G 27/005 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
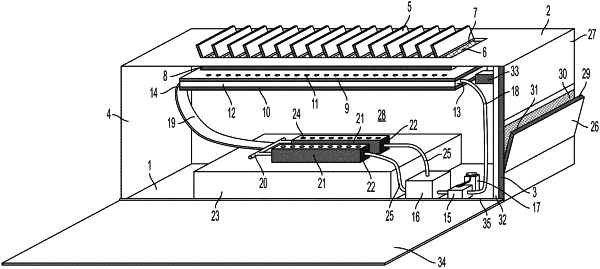
|
1. A hydroponic system comprising:
a) a support structure that has sides or walls that create an inner enclosed space that is separate from the outside environment, wherein:
i) the sides or walls have an inner surface that abuts the inner enclosed space and an opposite outer surface that abuts the outside environment;
ii) the inner enclosed space is accessible from the outside environment by a sealable opening in a side or wall of the support structure;
b) moveable warming panels which are integrated into the outer surface of a wall or side of the support structure such that, when moved to an open position, a gap is formed in the wall or side that allows the passage of air and sunlight from the outer environment into the inner enclosed space of the support structure and, when in a closed position, integrate into the side or wall to seal the gap;
c) an insect screen that is affixed to the inner surface of a wall or side of the support structure, wherein the insect screen is positioned to cover the gap formed when a panel is in an open position and has a mesh that allows the passage of air and sunlight but that prevents insects from passing from the outer environment into the inner closed space of the system;
d) a top planar element and a bottom planar element that are joined at their ends and along their sides in a manner such that a nutrient fluid channel is formed between them through which fluid can flow, wherein the top planar element and bottom planar element are located below the insect screen and run coextensively with all or part of the wall, wherein:
i) the top planar element is closer to the insect screen and above the bottom planar element;
ii) the top planar element permits the passage of both sunlight and air;
iii) the bottom planar element permits the passage of sunlight and optionally allows the passage of air but does not permit the passage of nutrient fluid;
iv) the nutrient fluid channel has a nutrient fluid receiving end and an opposite nutrient fluid dispensing end wherein both the nutrient fluid receiving end and the nutrient fluid dispensing end optionally have one or more ports through which fluid can flow;
e) a plant growth conduit located below the nutrient channel of paragraph d) and comprising an upper surface with openings that support pots or other vessels in which plants are grown and an inner plant growth channel through which nutrient fluid can flow; wherein:
i) the plants are suspended in the plant growth conduit such that they are exposed to sunlight that has passed through the nutrient fluid channel and have roots that extend into the plant growth channel where they may contact nutrient fluid;
ii) the plant growth conduit has a fluid receiving end that is in fluid communication with the nutrient dispensing end of the nutrient fluid channel such that nutrient fluid may flow through the one or more ports located at the fluid dispensing end of the nutrient fluid channel and through one or more ports at the fluid receiving end of the plant growth channel;
iii) the plant growth conduit has a fluid dispensing end distal to and opposite its fluid receiving end, and that is positioned to receive fluid that has passed through the plant growth channel and direct it to a fluid recovery conduit;
f) a nutrient fluid reservoir which is in fluid communication with the fluid dispensing end of the plant growth channel through a recovery conduit, such that, during operation, nutrient fluid passes from the dispensing end of the plant growth channel and to the nutrient fluid reservoir;
g) a pump or pressurized tank that receives nutrient fluid from the nutrient fluid reservoir and is in fluid communication with the nutrient fluid receiving end of the nutrient channel through an ascending nutrient fluid conduit.
|