| CPC C07C 1/0485 (2013.01) [B01J 20/22 (2013.01); B01J 20/3425 (2013.01); B01J 20/3441 (2013.01); C01B 3/40 (2013.01); C01B 32/40 (2017.08); C25B 1/04 (2013.01); C25B 15/081 (2021.01); C01B 2203/0233 (2013.01); C01B 2203/0244 (2013.01)] |
| AS A RESULT OF REEXAMINATION, IT HAS BEEN DETERMINED THAT: |
| Claims 1-6 and 9 are determined to be patentable as amended. |
| Claims 7, 8 and 10, dependent on an amended claim, are determined to be patentable. |
|
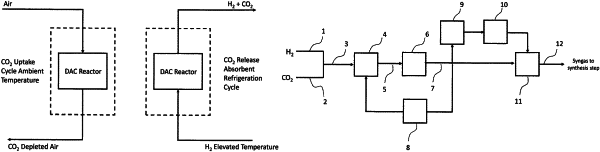
1. An integrated process for the conversion of feed streams comprising air, electricity, and water to a product stream comprising hydrocarbons, the process comprising:
a. an electrolysis step where an electrolyzer feed stream comprising water is converted to an electrolyzer product stream comprising hydrogen and oxygen where at least a portion of the electricity used in the electrolysis step is from renewable sources;
b. a direct air capture step where air is contacted with an adsorbent and carbon dioxide is removed from the air stream;
c. a reverse water gas shift step where at least a portion of the hydrogen from the electrolyzer product stream is reacted with a stream comprising carbon dioxide from the direct air capture step to produce a reverse water gas shift product stream comprising carbon monoxide;
d. a hydrocarbon synthesis step where at least a portion of the hydrogen from the electrolyzer product stream is reacted with a stream comprising at least a portion of the reverse water gas shift product stream [ and a catalyst ] to produce a hydrocarbon synthesis product stream [ comprising hydrocarbons, where the catalyst comprises a promoter and cobalt, nickel or a combination of nickel and cobalt, and where the catalyst is supported on alumina or silica, and where the alumina or silica has a pore diameter greater than 8 nm, and where carbon selectivity to CO2 in the hydrocarbon synthesis step is less than 1 percent of converted carbon monoxide] ;
e. an auto-thermal reforming step where at least a portion of the oxygen produced by electrolysis is reacted with a stream or streams comprising unreacted reactants from the hydrocarbon synthesis step.
|
|
2. The process of claim 1 where the direct air capture step uses a solid supported amine adsorbent [ , where the alumina or silica is lobed, and where the promoter is included at a concentration less than 0.1 weight percent] .
|
|
3. The process of claim 2 where the solid supported amine adsorbent is regenerated using a stream that comprises hydrogen produced in the electrolyzer [ , and where the reverse water gas shift step is performed in a reverse water gas shift reactor, and where there is a per pass conversion of CO2 to CO in the reverse water gas shift reactor, and where the per pass conversion is 70 percent to 90 percent] .
|
|
4. The process of claim 1 where the direct air capture uses aqueous KOH to remove carbon dioxide from the air [ , where the reverse water gas shift step is performed in a reverse water gas shift reactor comprising a catalyst, and where the catalyst is a solid solution catalyst comprising a transition metal on a metal oxide support] .
|
|
5. The process of claim 1 where the electrolyzer is in location 1 and the direct air capture is in location 2 and hydrogen from the electrolyzer is transported from location 1 to location 2 by an LOHC process [ , and where the reverse water gas shift step is performed in a reverse water gas shift reactor, and where the hydrogen from the electrolyzer product stream is heated to a temperature greater than 1600° F. using a radiant furnace before it enters the reverse water gas shift reactor] .
|
|
6. The process
|
|
9. The process of claim 1 where the auto-thermal reforming step includes steam as a feed where the steam to carbon ratio is 0.40-1.00 [ , where the auto-thermal reforming step provides an auto-thermal reforming product] .
|