| CPC G06T 7/11 (2017.01) [G06T 7/0012 (2013.01); G06T 7/136 (2017.01); G06V 10/26 (2022.01); G16H 30/40 (2018.01); G06T 2207/30024 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
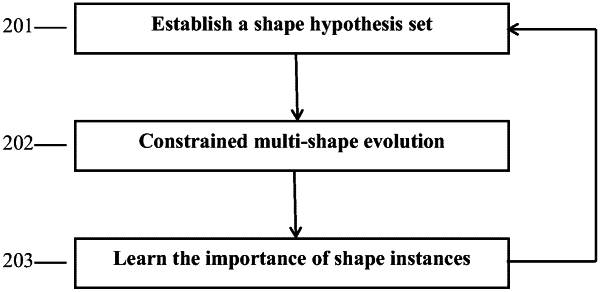
1. A method for segmenting overlapping cytoplasm in a medical image comprising:
establishing a cytoplasm shape hypothesis set; and
selecting a shape hypothesis for each cytoplasm from the established cytoplasm shape hypothesis set to perform constrained multi-shape evolution, thereby segmenting overlapping cytoplasm in the medical image, wherein the constrained multi-shape evolution comprises the following steps:
clump area segmentation performed to segment a clump area composed of a plurality of overlapping cytoplasm in the medical image to provide clump evidence;
shape alignment performed to assess quality of the selected shape hypothesis; and
shape evolution performed to determine a better shape hypothesis for each cytoplasm;
wherein the shape alignment and the shape evolution are performed iteratively, an output of the shape alignment is used as an input of the shape evolution, and an output of the shape evolution is used as an input of the shape alignment; the shape alignment assesses whether to start a new shape evolution or not, and once it is determined that no new shape evolution is required, a current shape hypothesis after the shape alignment is regarded as a segmentation result of the overlapping cytoplasm;
wherein the cytoplasm shape hypothesis set is established with a formula as follows:
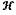 s={si:si=μ+Mxi, i∈ s={si:si=μ+Mxi, i∈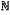 } }where μ represents an average shape of collected shape instances, Mxi represents a linear combination of eigenvectors of a covariance matrix of the collected shapes, wherein each column of the matrix M represents an eigenvector, xi represents a weight vector of the linear combination, and si represents a shape hypothesis marked as i; and
wherein the shape alignment comprises filling the shape hypotheses selected from the cytoplasm shape hypothesis set to obtain a binary image, and obtaining a rotation angle and a scaling size required for aligning the binary image with the corresponding cytoplasm with a formula as follows:
argmax(Bi∩Bc), s. t. Bi⊂Bc
where Bc represents an image of the segmented clump area; Bi represents an alignment result image, Bi is a binary image with the same size as Bc, and Bi should be inside Bc.
|