| CPC G01S 19/44 (2013.01) [G01S 17/931 (2020.01); G01S 19/45 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
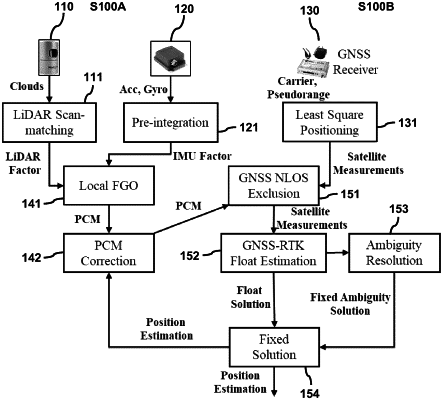
1. A method, used by a vehicle, for supporting positioning of the vehicle using a satellite positioning system, the method comprising:
receiving a LiDAR factor and an inertial measurement unit (IMU) factor, from a 3D LiDAR sensor and a LiDAR inertial odometry (LIO);
integrating the LiDAR factor and the IMU factor using a local factor graph optimization for estimating a relative motion between two epochs;
generating a 3D point cloud map (PCM) as an auxiliary landmark satellite for providing a low elevation auxiliary landmark satellite;
receiving global navigation satellite system (GNSS) measurements from satellites, by a GNSS receiver;
detecting a GNSS non-line-of-sight (NLOS) reception from the GNSS measurements using the 3D PCM; and
excluding the GNSS NLOS reception from the GNSS measurements to obtain survived GNSS satellite measurements for enhancing GNSS measurement quality for the positioning of the autonomous driving vehicle.
|