| CPC C01B 3/24 (2013.01) [C01B 32/05 (2017.08); C10B 19/00 (2013.01); C10B 57/16 (2013.01); C01B 2203/0272 (2013.01); C01B 2203/049 (2013.01); C01B 2203/06 (2013.01); C01B 2203/0855 (2013.01); C01B 2203/1241 (2013.01); C01B 2203/1604 (2013.01); C01B 2203/1614 (2013.01); C01B 2203/80 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
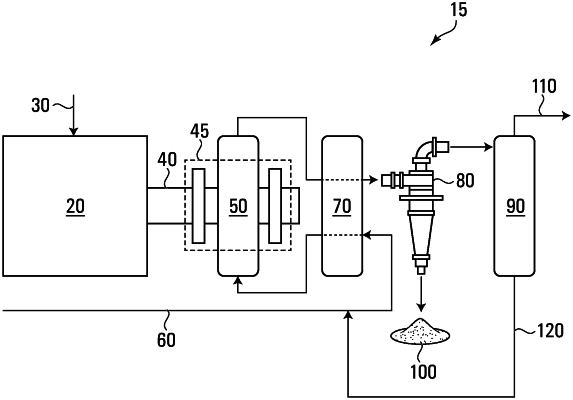
1. A method for preparing hydrogen and solid carbon, the method comprising:
a) providing a reaction vessel so that the reaction vessel has 0 wt % water and 0 wt % molecular oxygen inside the reaction vessel;
b) providing a feedstock comprising gaseous hydrocarbons to the reaction vessel, the reaction vessel having a starting solid carbon, 0 wt % water and 0 wt % molecular oxygen inside the reaction vessel, and the starting solid carbon being operable to heat the feedstock comprising gaseous hydrocarbons;
c) exposing the starting solid carbon in the reaction vessel to microwaves until the starting solid carbon is at a temperature of at least 1200 Kelvin, wherein the starting solid carbon is the primary microwave susceptor;
d) breaking carbon-hydrogen bonds of the gaseous hydrocarbons of the feedstock by heat transfer between the starting solid carbon and the gaseous hydrocarbons, thereby forming hydrogen and a prepared solid carbon in the reaction vessel; and
e) separating the hydrogen and the prepared solid carbon,
wherein the reaction vessel is microwave inert; and
wherein the method is conducted in a single-reactor system, wherein the single reactor is the reaction vessel.
|