| CPC B01D 41/00 (2013.01) [B08B 3/044 (2013.01); B08B 7/0071 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
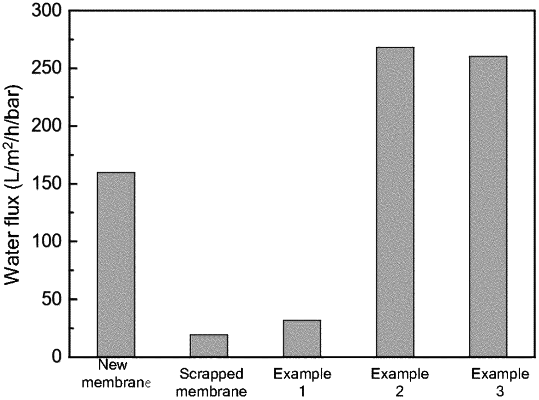
|
1. A method for recycling a scrapped polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane produced in a water treatment, comprising following steps:
1) a cleaning of the scrapped PVDF membrane: soaking the scrapped PVDF membrane in 0.2 wt % to 1.0 wt % sodium hypochlorite for 0.5 h to 4 h and then in 0.5 wt % to 4.0 wt % citric acid for 0.5 h to 4 h to remove mud cakes attached to a surface of the scrapped PVDF membrane to obtain a first cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane; and rinsing the first cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane with deionized water to obtain a second cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane for later use;
2) a structural transformation of the second cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane: soaking the second cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane treated in step 1) in a structural transformation agent at 10° C. to 40° C. for 0.5 min to 4.0 min to obtain a third cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane, wherein, irreversible contaminants are washed away while the second cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane is subjected to a pore expansion and a hydrophilization; and thoroughly rinsing the third cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane with the deionized water to remove superficial residual agents to obtain a fourth cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane; and
3) a hydrophilicity repairing of the fourth cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane: dissolving dopamine in a 15 mM Tris-HCl buffer aqueous solution to obtain a dopamine solution with a concentration of 0.4 mg/mL to 4 mg/mL, soaking the fourth cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane in the dopamine solution under a heating to obtain a mixture, and shaking the mixture in a shaker to obtain a repaired PVDF membrane, wherein, a polydopamine (PDA) hydrophilic layer is formed through a self-polymerization of the dopamine on a surface of the fourth cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane, the PDA hydrophilic layer further improves hydrophilicity of the surface of the fourth cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane, enhances an anti-contamination performance, and repairs damaged points on the surface of the fourth cleaned scrapped PVDF membrane produced during a long-term operation; and after the self-polymerization is completed, rinsing the repaired PVDF membrane with running deionized water to remove weakly-bound PDA.
|