| CPC A61N 5/0624 (2013.01) [A61N 2005/063 (2013.01); A61N 2005/0652 (2013.01); A61N 2005/0661 (2013.01); A61N 2005/0666 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
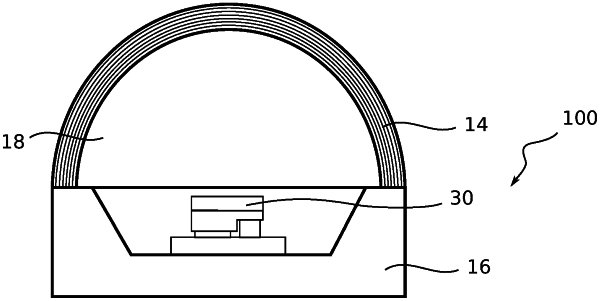
1. A device for UV antisepsis, comprising:
a light-emitting diode chip (LED chip) configured to emit radiation in the UVC spectral range, wherein the LED chip forms a light-emitting diode (LED) with a package, wherein the LED chip has been grown on a substrate of bulk AlN or sapphire;
a spectral filter element set up substantially to limit the radiation emitted by the LED chip to wavelengths below 235 nm by means of largely angle-independent spectral filtering,
wherein the spectral filter element is integrated as an AlOx/SiO2-DBR or as a DBR filter with HfO2, Ta2O5, CaF2, MgF2, Ga2O3 or AlN as dielectric into the package of the LED or is applied to the LED chip, wherein the shape of the spectral filter element is adapted to the emission characteristics of the LED such that an optical path length traversed by the radiation across the spectral filter element is essentially the same for all spatial directions;
and
an optical element for directional emission of the radiation emitted by the LED, wherein spatial uniformity of radiant power is achieved by adapting emission to an area to be irradiated by means of the device.
|
|
12. A device for UV antisepsis, comprising:
a light-emitting diode chip (LED chip) configured to emit radiation in the UVC spectral range, wherein the LED chip forms a light-emitting diode (LED) with a package, wherein the LED chip has been grown on a substrate of bulk AlN or sapphire;
a spectral filter element set up substantially to limit the radiation emitted by the LED chip to wavelengths below 235 nm by means of largely angle-independent spectral filtering, wherein the spectral filter element is integrated as an intrinsic Bragg reflector with a plurality of AlxGa1-xN/AlyGa1-yN layer pairs with x≠y into an epitaxial layer structure of the LED chip; and
an optical element for directional emission of the radiation emitted by the LED, wherein spatial uniformity of radiant power is achieved by adapting emission to an area to be irradiated by means of the device.
|
|
13. A device for UV antisepsis, comprising:
a light-emitting diode chip (LED chip) configured to emit radiation in the UVC spectral range, wherein the LED chip forms a light-emitting diode (LED) with a package, wherein the LED chip has been grown on a substrate of bulk AlN or sapphire;
a spectral filter element set up substantially to limit the radiation emitted by the LED chip to wavelengths below 235 nm by means of largely angle-independent spectral filtering, wherein the spectral filter element is obtained as an angle-independent bandpass filter via excitation of surface plasmons or a Fabry-Pérot filter; and
an optical element for directional emission of the radiation emitted by the LED, wherein spatial uniformity of radiant power is achieved by adapting emission to an area to be irradiated by means of the device.
|