| CPC A61H 31/005 (2013.01) [A61H 31/007 (2013.01); A61H 2201/0188 (2013.01); A61H 2201/5007 (2013.01); A61H 2201/5043 (2013.01); A61H 2201/5092 (2013.01); A61H 2230/20 (2013.01); A61H 2230/25 (2013.01)] | 54 Claims |
|
1. A system for managing a chest compression treatment to a patient in need of emergency assistance by a rescuer, the system comprising:
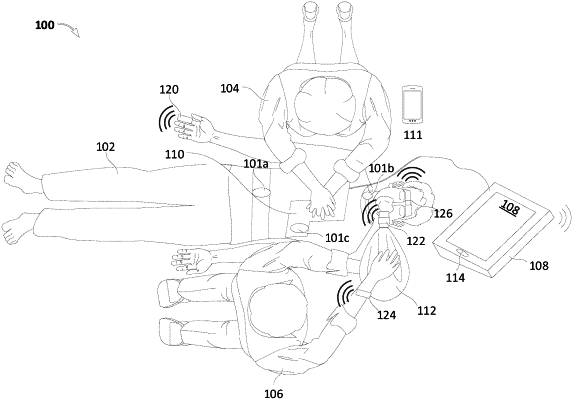
at least one sensor configured to measure blood flow data;
one or more computer executable media comprising instructions;
one or more processors, in communication with the at least one sensor, configured to execute the instructions by performing operations comprising:
receiving the blood flow data from the at least one sensor,
based on the blood flow data, generating arterial blood flow data and venous blood flow data,
determining an arterial blood flow peak based on the generated arterial blood flow data, wherein the arterial blood flow peak comprises a prominent peak among the generated arterial blood flow data for a compression cycle of the chest compression treatment,
determining a venous blood flow peak based on the generated venous blood flow data, wherein the venous blood flow peak comprises a prominent peak among the generated venous blood flow data for the compression cycle of the chest compression treatment,
providing an estimation of chest compression effectiveness based on the determined arterial blood flow peak and the venous blood flow peak, the estimation being based on a comparison of a time difference between the arterial blood flow peak and the venous blood flow peak, and
generating an output indication of the estimation of chest compression effectiveness; and
an output device configured to provide the output indication for the rescuer.
|
|
20. A method of detecting net forward blood flow during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) in a patient, the method comprising:
receiving, by one or more processors and from at least one sensor, blood flow data,
based on the blood flow data, generating, by the one or more processors, arterial blood flow data and venous blood flow data,
determining an arterial blood flow peak based on the generated arterial blood flow data, wherein the arterial blood flow peak comprises a prominent peak among the generated arterial blood flow data for a compression cycle of the chest compression treatment,
determining a venous blood flow peak based on the generated venous blood flow data, wherein the venous blood flow peak comprises a prominent peak among the generated venous blood flow data for the compression cycle of the chest compression treatment,
providing, by the one or more processors, an estimation of forward blood flow based on the arterial blood flow peak and the venous blood flow peak, the estimation being based on a comparison of a time difference between the arterial blood flow peak and the venous blood flow peak,
generating, by the one or more processors, an output indication of the estimation of the forward blood flow; and
providing, by the one or more processors, the output indication to be displayed to the rescuer.
|