| CPC H05H 3/02 (2013.01) [G04F 5/145 (2013.01); G21K 1/093 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
1. A magneto-optical trap method comprising steps of:
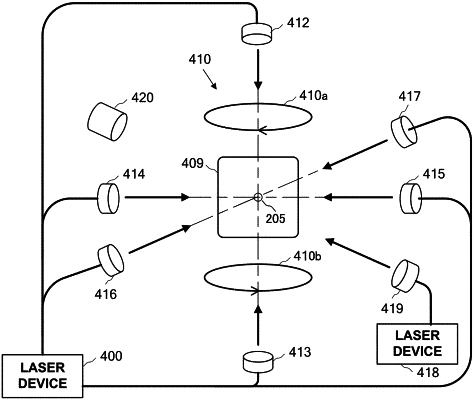
applying a magnetic field to an atom encapsulated in a vacuum vessel and having a nuclear spin of not less than 3/2 by using an anti-Helmholtz coil;
generating a laser beam including a first laser beam detuned from a first resonance frequency when the atom transits from a total angular momentum quantum number F in a ground state related to a hyperfine structure to a total angular momentum quantum number F′=F+1 in an excited state related to the hyperfine structure, and a second laser beam detuned from a second resonance frequency when the atom transits from the total angular momentum quantum number F in the ground state related to the hyperfine structure to a total angular momentum quantum number F′=F−1 in the excited state related to the hyperfine structure, among transitions of the atom from a total angular momentum quantum number J=0 in a ground state related to a fine structure to a total angular momentum quantum number J′=1 in an excited state related to the fine structure, by multiplexing the first laser beam and the second laser beam; and
irradiating the laser beam including the first laser beam and the second laser beam toward the atom in the vacuum vessel from a plurality of directions including at least a pair of opposite directions, and simultaneously making the first laser beam trap the atom in a state that a magnetic quantum number is negative, and the second laser beam trap the atom in a state that the magnetic quantum number is positive.
|