| CPC H04L 5/0048 (2013.01) [H04L 27/0008 (2013.01); H04L 27/2613 (2013.01); H04L 27/26025 (2021.01); H04L 27/2666 (2013.01); H04W 56/001 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
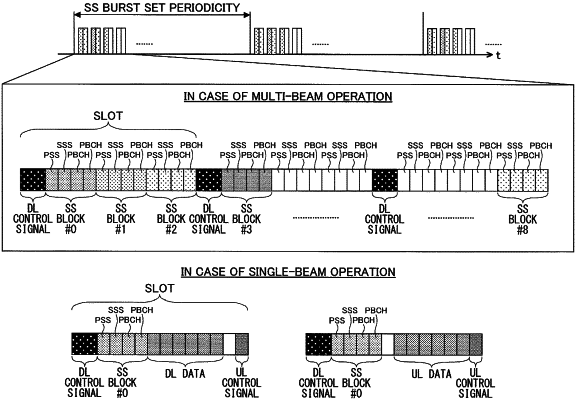
1. A terminal that uses a plurality of subcarrier spacings including 15 kHz, 30 kHz, 120 kHz, and 240 kHz, the terminal comprising:
a receiver that receives, based on one of the plurality of subcarrier spacings, one or more symbols to which periodic blocks including a synchronization signal and system information are mapped; and
a processor that performs random access by using a resource associated with the periodic blocks,
wherein a period during which the periodic blocks are mapped is arranged to be common across the subcarrier spacings,
wherein the receiver receives a signal in which a position of the symbols is determined on a basis of the subcarrier spacings, and
wherein a maximum number of the periodic blocks included in an SS burst in a case where the subcarrier spacing is 120 kHz is the same as a maximum number of periodic blocks included in the SS burst in a case where the subcarrier spacing is 240 kHz.
|