| CPC H01J 37/321 (2013.01) [H01J 37/32128 (2013.01); H01J 37/32146 (2013.01); H01J 37/32183 (2013.01); H01J 37/32577 (2013.01); H01L 21/3065 (2013.01); H01L 21/67069 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A system comprising:
a computer configured to generate a digital pulsed signal having a high bit state and a low bit state;
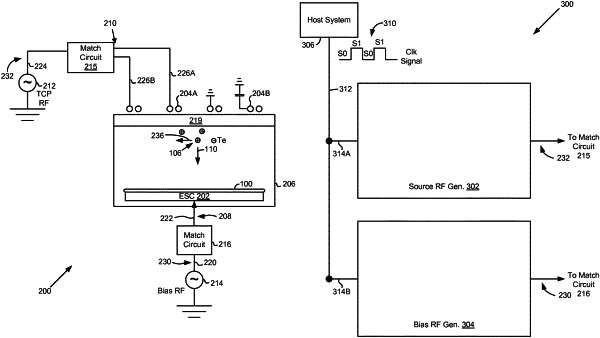
a source radio frequency (RF) generator coupled to the computer via a shared cable located between the computer and the source RF generator, wherein the source RF generator includes a processor and a source power supply, wherein the processor of the source RF generator is configured to receive the digital pulsed signal from the computer via the shared cable, wherein in response to the reception of the digital pulsed signal, the processor of the source RF generator is configured to control the source power supply to generate a source RF pulsed signal having a first high state and a low state in synchronization with the digital pulsed signal, wherein the first high state of the source RF pulsed signal has a greater amount of power than the low state of the source RF pulsed signal;
a plasma chamber coupled to the source RF generator, wherein the plasma chamber is associated with a top coil electrode and has a bottom electrode, wherein the source RF generator is coupled to the top coil electrode; and
a bias RF generator coupled to the computer via the shared cable located between the computer and the bias RF generator, wherein the bias RF generator includes a processor and a bias power supply, wherein the processor of the bias RF generator is configured to receive the digital pulsed signal via the shared cable, wherein the bias RF generator is coupled to the bottom electrode, wherein in response to the reception of the digital pulsed signal, the processor of the bias RF generator is configured to control the bias power supply to generate a bias RF pulsed signal in reverse synchronization with the digital pulsed signal, wherein the bias RF pulsed signal is generated to have the low state for a first time period during which the digital pulsed signal is in the high bit state, wherein the bias RF pulsed signal has a second high state for a second time period during which the digital pulsed signal is in the low bit state, wherein the second time period is equal to the first time period, wherein the second high state of the bias RF pulsed signal has a greater amount of power than the low state of the bias RF pulsed signal,
wherein the computer is configured to:
control the source RF generator to transition the source RF pulsed signal from the first high state to the low state at a time of transition of the digital pulsed signal from the high bit state to the low bit state, and
control the bias RF generator to transition the bias RF pulsed signal from the low state to the second high state at the time of transition of the digital pulsed signal from the high bit state to the low bit state, wherein the bias RF pulsed signal transitions from the low state to the second high state during a conductor etch to control directionality of ions of plasma and to reduce a temperature of electrons within the plasma,
wherein the processor of the bias RF generator is configured to determine that the digital pulsed signal transitions from the high bit state to the low bit state, and send a control signal to the bias power supply to transition the bias RF pulsed signal from the low state to the second high state in response to determining that the digital pulsed signal transitions from the high bit state to the low bit state.
|