| CPC G10L 25/69 (2013.01) [G10L 15/142 (2013.01); G10L 15/16 (2013.01); G10L 25/30 (2013.01); G10L 25/75 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
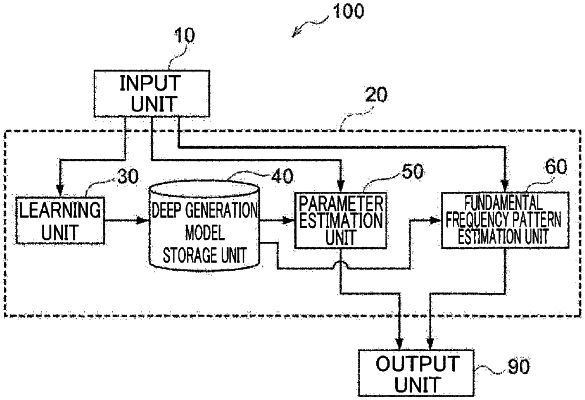
1. A computer-implemented method for estimating aspects of speech signal in voice data, the method comprising:
learning a deep generation model, wherein the deep generation model comprises:
an encoder, wherein the encoder estimates a first parameter included in a first fundamental frequency pattern of a first speech signal in a first input voice data, the first parameter corresponds to a latent variable of the deep generation model, and the learning of the deep generation model includes updating the latent variable of the deep generation model based on parallel data between the first fundamental frequency pattern of the first speech signal and the first parameter included in the first fundamental frequency pattern of the first speech signal as training data, and
a decoder, wherein the decoder reconstructs, based on the latent variable of the deep generation model, the first fundamental frequency pattern of the first speech signal in the first input voice data, wherein the latent variable of the deep generation model corresponds to the first parameter included in the first fundamental frequency pattern of the first speech signal;
estimating, based on a second fundamental frequency pattern of a second speech signal in a second input voice data for encoding and subsequently for reconstructing, a second parameter included in the second fundamental frequency pattern using the encoder of the learnt deep generation model; and
estimating, based on the second parameter included in the second fundamental frequency pattern of speech signal in the second input voice data, the second fundamental frequency pattern using the decoder of the deep generation model to reconstruct the second fundamental frequency pattern associated with the second input voice data.
|