| CPC G06T 5/50 (2013.01) [G06T 7/55 (2017.01); G06T 2207/10024 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10048 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20221 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
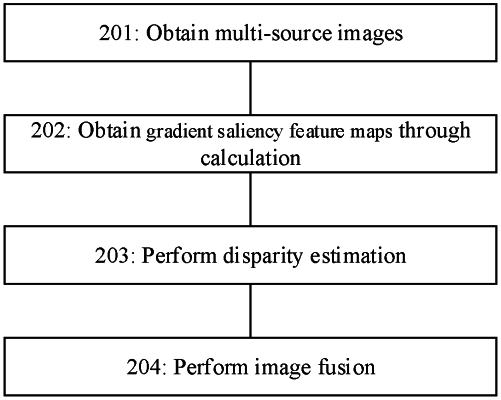
1. An image processing method, comprising:
obtaining a first image;
obtaining a second image;
extracting a first vertical gradient and a first horizontal gradient of each band in the first image using a first gradient operator;
extracting a second vertical gradient and a second horizontal gradient of each band in the second image using a second gradient operator;
calculating a first gradient saliency feature map of each band in the first image based on the first vertical gradient and the first horizontal gradient;
performing weighted averaging on each pixel in the first gradient saliency feature map of each band in the first image to obtain a first gradient saliency map of the first image;
calculating a second gradient saliency feature map of each band in the second image based on the second vertical gradient and the second horizontal gradient;
performing weighted averaging on each pixel in the second gradient saliency feature map of each band in the second image to obtain a second gradient saliency map of the second image;
performing, based on the first gradient saliency feature map and the second gradient saliency feature map, feature matching between the first image and the second image to obtain a dense disparity map of the first image;
performing disparity translation on a second pixel in the second image corresponding to a first pixel in the first image based on the dense disparity map; and
fusing, based on the dense disparity map, the first image and the second pixel.
|