| CPC G01N 29/036 (2013.01) [G01N 29/024 (2013.01); G01N 29/222 (2013.01); G01N 29/2437 (2013.01); G01N 2291/011 (2013.01); G01N 2291/014 (2013.01); G01N 2291/021 (2013.01); G01N 2291/02881 (2013.01); G01N 2291/102 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A method of measuring gas characteristics at low pressure atmospheres, the steps comprising:
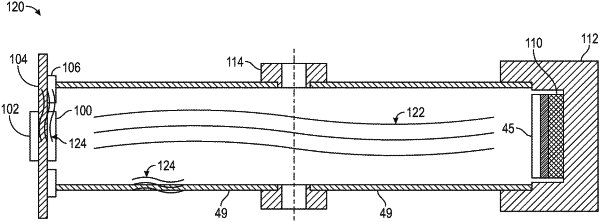
providing an air path chamber having a first speaker located on a substrate on a first end of the air path chamber, a first microphone located within the air path chamber on a second end of the air path chamber opposite the first speaker, a conductive chamber extending outward from the first speaker at a first end of the conductive chamber, opposite the air path chamber and having a second microphone at a second end of the conductive chamber;
inserting a gas into the air path chamber;
initiating a first sound wave within the air path chamber through the first speaker;
receiving the first sound wave at the first microphone located within the air path chamber;
receiving a second sound wave produced by the first speaker at the second microphone located within the conductive chamber;
calculating a frequency of the first sound wave;
calculating the speed of the first sound wave;
calculating a k/M ratio of the gas;
calculating a temperature of the gas based upon the k/M ratio, frequency and speed of the sound wave;
amplifying the first sound wave received at the first microphone and amplifying the second sound wave at the second microphone; and
calculating a summed sound wave by subtracting the first received sound wave at the first microphone from the second received sound wave at the second microphone.
|