| CPC C04B 20/1037 (2013.01) [C01B 33/18 (2013.01); C04B 14/062 (2013.01); C04B 28/04 (2013.01); C04B 40/0032 (2013.01); B82Y 30/00 (2013.01); B82Y 40/00 (2013.01); C04B 20/0008 (2013.01); C04B 40/0082 (2013.01); E21B 33/14 (2013.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
1. A method of using a nanosilica-containing cement in an well cementing operation, the method comprising the steps of:
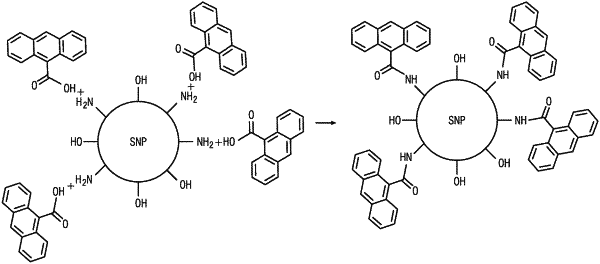
mixing encapsulated nanosilica and a cement formulation to produce the nanosilica-containing cement formulation, where the encapsulated nanosilica comprises determinant nanosilica particles encapsulated by a reversible cage, where the reversible cage comprises a functional coating,
where the functional coating comprises a polyetheramine and a functional moiety selected from the group consisting of a furfuryl moiety, an anthracene moiety, a maleimide moiety, and combinations of the same,
where the reversible cage is formed through a reversible reaction selected from the group consisting of a reversible covalent reaction, a non-covalent reaction, and combinations of the same,
where the determinant nanosilica particles are selected from the group consisting of silica nanoparticles, functionalized silica nanoparticles, and combinations of the same;
pumping the nanosilica-containing cement formulation into the oil well;
increasing a temperature in the oil well to initiate the disintegration of the reversible cage, wherein the temperature is increased to greater than 130° C.;
exposing the determinant nanosilica particles due to the disintegration of the cage from the encapsulated nanosilica; and
reacting the determinant nanosilica particles with the cement formulation such that gelation of the cement formulation occurs.
|