| CPC G06Q 50/02 (2013.01) [G06Q 10/04 (2013.01); G06Q 30/018 (2013.01); Y02P 90/84 (2015.11)] | 20 Claims |
|
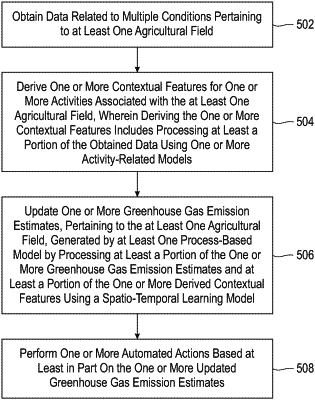
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
obtaining data related to multiple conditions pertaining to at least one agricultural field;
deriving one or more contextual features for one or more activities associated with the at least one agricultural field, wherein deriving the one or more contextual features comprises processing at least a portion of the obtained data using one or more activity-related models, and wherein deriving the one or more contextual features comprises deriving one or more contextual features for weeding-related activity and deriving one or more contextual features for at least one of soil disturbance activity, temperature inversion activity, pest-related activity, and disease-related activity;
updating one or more greenhouse gas emission estimates, pertaining to the at least one agricultural field, generated by at least one process-based model by processing at least a portion of the one or more greenhouse gas emission estimates and at least a portion of the one or more derived contextual features using a spatio-temporal learning model, wherein the spatio-temporal learning model comprises at least one neural network, and wherein updating the one or more greenhouse gas emission estimates comprises updating the one or more greenhouse gas emission estimates based at least in part on one or more greenhouse gas emission quantity updates and one or more greenhouse gas emission temporal updates, wherein the one or more greenhouse gas emission temporal updates comprise one or more contextual feature-effected time delay corrections to the one or more greenhouse gas emission estimates generated by the at least one process-based model, the one or more contextual feature-effected time delay corrections being related to forecasted timing of greenhouse gas emission relative to performance of at least one of the one or more activities associated with the at least one agricultural field; and
performing one or more automated actions based at least in part on the one or more updated greenhouse gas emission estimates, wherein performing the one or more automated actions comprises automatically training the spatio-temporal learning model using at least a portion of the one or more updated greenhouse gas emission estimates;
wherein the method is carried out by at least one computing device.
|