| CPC G06F 11/301 (2013.01) [G06F 3/0647 (2013.01); G06F 8/60 (2013.01); G06F 9/45533 (2013.01); G06F 9/50 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06F 2009/4557 (2013.01); G06F 11/3495 (2013.01); G06F 2206/1012 (2013.01); G06F 2206/1508 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
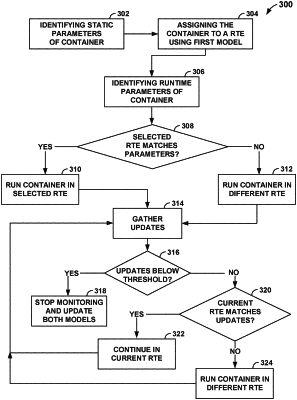
identifying static parameters of a software container, wherein the static parameters relate to metadata of the software container itself;
assigning the software container to a selected runtime environment based on the static parameters using a first machine learning model;
identifying runtime parameters for the software container by analyzing the software container at runtime, where the runtime parameters relate to operations required during runtime by the software container;
using a second machine learning model, in response to a determination that the selected runtime environment matches the runtime parameters, and continuing to run the software container in the selected runtime environment;
using the second machine learning model, in response to a second determination that the selected runtime environment does not match the runtime parameters, running the software container in a different runtime environment that matches both the static and runtime parameters;
gathering, on a predetermined schedule, characteristics of the software container with correlations that dictate performance changes in the different runtime environment; wherein the characteristics include stability of the different runtime environments and latency for each runtime environment introduced by a computer processing contention;
generating training data based on the correlations between the characteristics and the performance changes in the different runtime environment; and
retraining the second machine learning model based on the training data.
|