| CPC G01V 1/01 (2024.01) [G01H 9/004 (2013.01); G01V 1/282 (2013.01); G01V 1/307 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
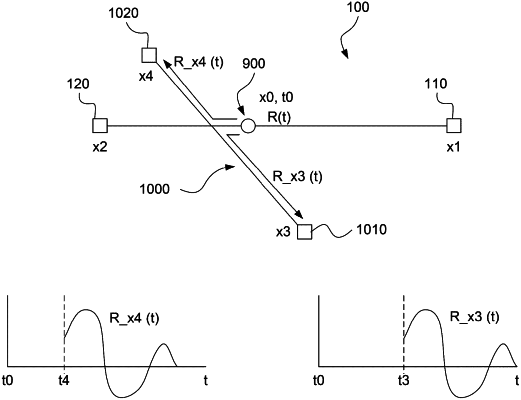
1. A method of evaluating undersea seismic activity comprising:
receiving, by one or more processors, one or more optical signals from one or more stations located along an underwater optical route, each of the one or more optical signals having a polarization state that can be represented as one or more time series over a duration of time, each of the one or more time series corresponding to a respective Stokes parameter; and
detecting, by the one or more processors, occurrence of a seismic event using a machine learning model based on an analysis of the one or more time series of the polarization states of the one or more optical signals, wherein the machine learning model is trained on prior examples of seismic activity.
|