| CPC F02K 9/10 (2013.01) [B64G 1/404 (2013.01); F02K 9/18 (2013.01); F02K 9/24 (2013.01); F02K 9/28 (2013.01); F02K 9/34 (2013.01); F02K 9/72 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
1. A fuel grain for a rocket, the fuel grain comprising:
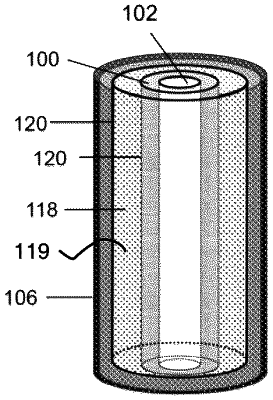
a cylindrical shell housing a plurality of layers of fuel grain material, each layer comprising a plurality of concentric circular structures of different diameter fused together to form a central opening therein;
wherein the fuel grain material comprises an electrically ignitable substance; the plurality of layers stacked and joined securely to form a cylindrical fuel grain with the central opening of each one of the plurality of layers aligned to form a combustion unit extending axially through the fuel grain and bounded by a combustion surface;
a series of annular sections housed within the cylindrical shall, the annular sections having spaces between them filled with the electrically ignitable substance; wherein the annular sections comprise embedded electrodes and embedded sensors; wherein the embedded sensors indicate relative stabilizer depletion, internal off-gassing, internal swelling, and pressure buildup;
a central chamber formed at least in part by the plurality of layers, each layer having a series of abutting and interwoven surfaces of solidified fuel grain material arrayed around the central chamber to increase the surface area of the combustion surface;
wherein the fuel grain includes heterogenous materials having unfilled thermoplastics and filled thermoplastics to enhance thrust performance;
wherein the heterogenous materials further comprise propellants; wherein the propellants comprise electrically activated solid propellant; wherein the propellant is additively manufactured in conjunction with the sensors;
wherein the electrically activated solid propellant is ignited by the embedded electrodes;
wherein increase in surface area of the combustion surface improves regression rate, specific impulse, generates an oxidizer vortex flow, and reduces fuel waste by inducing oxidizer axial flow within the center chamber to allow more time for oxidizer and fuel gases to mix and combust thoroughly.
|