| CPC C23F 11/167 (2013.01) [C23C 16/0272 (2013.01); C23C 16/06 (2013.01); C23C 16/56 (2013.01); F02C 7/00 (2013.01); F16L 58/04 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A gas turbine engine comprising a component configured to be in contact with a hydrocarbon fluid, the component comprising:
a wall having a contact surface configured to be in contact with the hydrocarbon fluid, the contact surface being formed from a metal, the metal comprising a metal M, wherein M is selected from the group consisting of nickel (Ni), palladium (Pd), and platinum (Pt); and
a metal-ligand complex on the contact surface, the metal-ligand complex comprising phosphorus (P),
wherein the component is at least one of a fuel nozzle, a swirler, or an oil scavenge line.
|
|
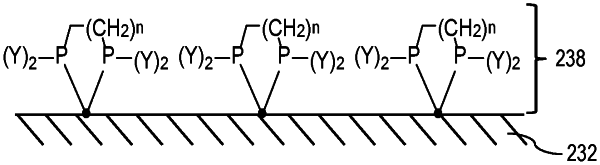
16. A component configured to be in contact with a hydrocarbon fluid, the component comprising:
a wall having a contact surface configured to be in contact with the hydrocarbon fluid, the contact surface being an outermost layer formed on a surface of the wall and being formed from a metal, the metal comprising a metal M, wherein M is selected from the group consisting of nickel (Ni), palladium (Pd), and platinum (Pt); and
a metal-ligand complex on the contact surface, the metal-ligand complex has having the following structure:
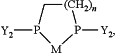 wherein n is an integer from 1-3; each Y is independently —R, —OR, —SR, and —NR′2 with R being an alkyl group or aryl group optionally substituted with one or more heteroatoms; and R′ being one of hydrogen (H) and R.
|
|
19. A component configured to be in contact with a hydrocarbon fluid, the component comprising:
a wall having a contact surface configured to be in contact with the hydrocarbon fluid, the contact surface being an outermost layer formed on a surface of the wall and being formed from a metal, the metal comprising a metal M, wherein M is selected from the group consisting of nickel (Ni), palladium (Pd), and platinum (Pt);
a metal-ligand complex on the contact surface, the metal-ligand complex comprising phosphorus (P); and
a ceramic barrier layer between the outermost layer and the wall.
|