| CPC B01F 35/213 (2022.01) [B01F 35/2208 (2022.01); G01N 29/024 (2013.01); G01N 29/032 (2013.01); G01N 29/46 (2013.01); G01N 2291/011 (2013.01); G01N 2291/015 (2013.01); G01N 2291/02416 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
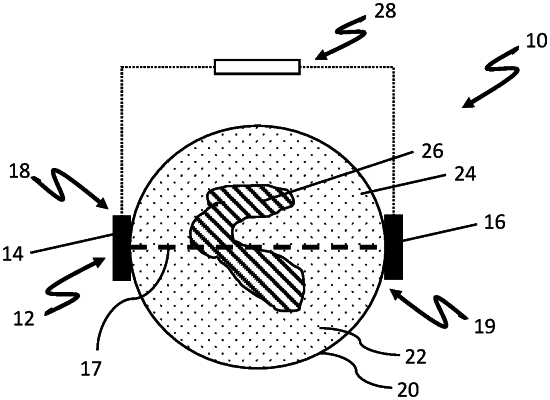
1. A method of determining a mixing state of a medium in a container, the method comprising the steps of:
transmitting a plurality of acoustic signals at least partly through the medium and receiving the plurality of acoustic signals after at least partly traversing the medium;
determining at least one propagation value of at least one propagation quantity for each of the plurality of received acoustic signals to provide determined propagation values, each at least one propagation quantity being indicative of an interaction of the acoustic signals with the medium, wherein the acoustic signals are transmitted at least partly through the medium in a sequence of time;
determining at least one fluctuation value of at least one fluctuation quantity based on the determined propagation values to provide a determined at least one fluctuation value, each at least one fluctuation quantity being indicative of and/or correlating with a variance of the determined propagation values and/or with a state of a mixture;
determining the mixing state of the medium based on the determined at least one fluctuation value, the mixing state being indicative of a homogeneity the medium;
determining a time series of the determined propagation values of the acoustic signals;
determining a time period between at least two extrema of the time series of the propagation values; and
determining a rotational speed of the medium, at which the medium rotates, based on the determined time period between the at least two extrema of the time series of the propagation values.
|