| CPC A61B 34/10 (2016.02) [A61B 34/25 (2016.02); A61B 34/37 (2016.02); A61B 2034/107 (2016.02)] | 7 Claims |
|
1. A system for an interventional procedure using medical images, the system comprising:
a robot arm provided with a medical tool, and configured to operate such that the medical tool follows intervention trajectories;
a master device configured to perform control so that the medical tool of the robot arm follows the intervention trajectories;
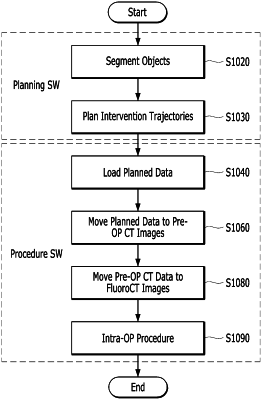
an image processing device configured to:
register plan images, in which a surgical plan including the intervention trajectories of the medical tool is set up, and preoperative (pre-op) images acquired at a surgical site before surgery so that the surgical plan is transferred to the pre-op images; and
register the pre-op images and intraoperative (intra-op) images acquired at the surgical site during the surgery; and
a user interface device configured to visualize a predicted arrival location of a tip of the medical tool for a target point when the robot arm operates according to the surgical plan by using the pre-op images, to which the surgical plan has been transferred, and the intra-op images in conjunction with the image processing device,
wherein the image processing device is further configured to:
distinguish a first area and a second area in the pre-op images before the registration of the pre-op images and the plan images, based on correlations of each of the first area and the second area with the surgical plan, wherein anatomical structures in the second area are on the intervention trajectories or a procedure target area of the surgical plan whereas anatomical structures in the first area are not;
for the first area, identify second anatomical structures based on a segmentation-based identification by performing image segmentation instead of a registration-based identification; and
for the second area, register third anatomical structures in the second area and first anatomical structures corresponding to the third anatomical structures in the plan images.
|