| CPC A61B 8/481 (2013.01) [A61B 8/0808 (2013.01); A61B 8/5207 (2013.01); A61N 7/02 (2013.01); A61N 2007/0039 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
1. A method of monitoring delivery of a therapeutic agent to a brain of a subject, the method comprising:
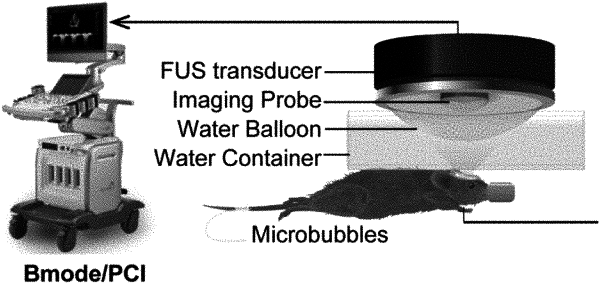
treating the brain of the subject with a focused ultrasound in combination with microbubbles for blood-brain barrier disruption (FUS-BBBD);
administering the therapeutic agent to the subject;
obtaining a spatial map of a stable cavitation dose (SCD) using a passive cavitation imaging (PCI) system; and
transforming the spatial map of the stable cavitation dose (SCD) to a map of a concentration of the therapeutic agent delivered to the brain of the subject using a pre-determined correlation of the stable cavitation dose (SCD) and the concentration of the therapeutic agent delivered to the brain of the subject, wherein the map of the concentration of the therapeutic agent is obtained in real time while modulating the treatment of the brain of the subject in real time.
|