| CPC H04W 72/51 (2023.01) [G08G 5/0013 (2013.01); G08G 5/0069 (2013.01); H04W 72/0453 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
1. A dynamic channel assignment method of a point-to-multipoint (P2MP) unmanned aircraft system (UAS) comprising a spectrum authority, a ground control station (GCS), a ground radio station (GRS) supporting a plurality of unmanned aircrafts, and an unmanned aircraft, the method comprising:
transmitting, at the GRS, information of the GRS to the spectrum authority, and receiving assignment of an uplink frequency set from the spectrum authority;
registering, at the spectrum authority, the uplink frequency set and information of the GRS to a database of the spectrum authority;
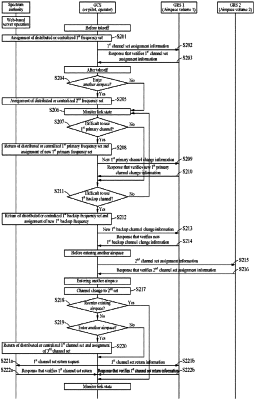
receiving, at the GCS, assignment of a first communication channel set for communication between the GCS and the unmanned aircraft from the spectrum authority before takeoff of the unmanned aircraft;
receiving, at the GCS, assignment of a second communication channel set before the unmanned aircraft enters a second area when the unmanned aircraft is to move from a first area in which the first communication channel set is available to the second area in which the second communication channel set different from the first communication channel set is available due to a flight plan of the unmanned aircraft after takeoff of the unmanned aircraft;
performing, at the GCS, communication with the unmanned aircraft using the second communication channel set when the unmanned aircraft enters the second area;
maintaining, at the GCS, the first communication channel set when the unmanned aircraft reenters the first area from the second area due to the flight plan of the unmanned aircraft, and returning, at the GCS, the first communication channel set to the spectrum authority when the unmanned aircraft does not reenter the first area due to the flight plan of the unmanned aircraft; and
monitoring, at the GCS, a link state of a communication channel set in use,
wherein the communication channel set includes a primary channel and a backup channel,
wherein monitoring, at the GCS, includes monitoring a signal interference and noise ratio (SINR) of the primary channel and requesting the spectrum authority for another primary channel, different from the primary channel, based on the SINR of the primary channel, and
wherein monitoring, at the GCS, includes monitoring a SINR of the backup channel and requesting the spectrum authority for another backup channel, different from the backup channel, based on the SINR of the backup channel.
|