| CPC H02K 11/33 (2016.01) [H02K 1/12 (2013.01); H02K 1/22 (2013.01); H02K 11/27 (2016.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
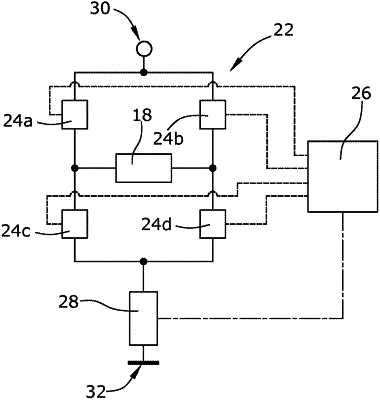
1. A method for driving a single-phase electric motor, the single phase electric motor comprising:
a static motor stator comprising a stator coil;
a rotatable motor rotor;
a switchable drive electronics which is electrically connected to the stator coil and which is configured to energize the stator coil with a pulse-width-modulated drive energy signal, for driving the rotatable motor rotor, the drive energy signal having a defined effective duty cycle;
a control electronics which is configured to switch the switchable drive electronics so as to generate the pulse-width-modulated drive energy signal; and
a current sensor which is configured to measure a phase current flowing through the stator coil,
the method comprising:
switching the switchable drive electronics to a first on-state during a first on-time interval of a pulse width modulation period of the pulse-width-modulated drive energy signal;
switching the switchable drive electronics to a second on-state during a second on-time interval of the pulse width modulation period;
switching the switchable drive electronics to an off-state between the first on-time interval and the second on-time interval; and
measuring the phase current with the current sensor,
wherein,
the first on-time interval and the second on-time interval of one pulse width modulation period are provided with a same interval length if the defined effective duty cycle is higher than or equal to a first duty threshold value and are provided with different interval lengths if the defined effective duty cycle is lower than the first duty cycle threshold value so as to provide that at least one of the first on-time interval and the second on-time interval is provided with an interval length which is equal to or larger than a defined minimum on-time interval length, and
the phase current is measured during the at least one of the first on-time interval and the second on-time interval which is provided with the defined minimum on-time interval length.
|