| CPC G16C 20/70 (2019.02) [G16C 20/10 (2019.02); G16C 20/40 (2019.02); G16C 20/50 (2019.02); G16C 60/00 (2019.02); B01J 29/04 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A computer implemented method for catalyst construction, the method comprising:
extracting historical data including historic chemical reaction data and historic catalyst construction yield data;
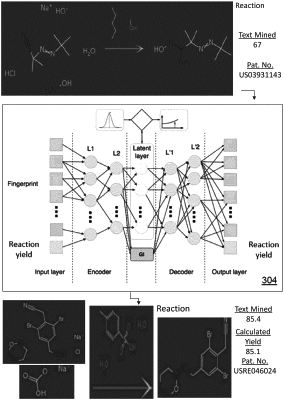
converting the historic chemical reaction data into graph models to represent molecular structure data;
incorporating the graph models representing the molecular structure data into a chemical reaction algorithm;
training a vectorized cognitive deep learning network of the chemical reaction algorithm by using the graph models and a property of the historic chemical reaction data to produce a catalyst chemical reaction model;
validating the catalyst chemical reaction model by inputting the historic chemical reaction data and comparing a generated property corresponding to the catalyst chemical reaction model to the property of the historic chemical reaction data; and
updating, based on a difference between the generated property and the property of the historic chemical reaction data being larger than a threshold value, the training of the catalyst chemical reaction model.
|