| CPC G08G 1/0133 (2013.01) [B60W 60/00276 (2020.02); G08G 1/015 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
1. A method for predicting a trajectory of a traffic participant in a complex heterogeneous environment, comprising the following steps:
obtaining traffic participant information in a complex heterogeneous environment, wherein the traffic participant information comprises position information, velocity information, acceleration information, and class information;
arranging and numbering traffic participant classes based on the class information, to obtain serial numbers of the traffic participant classes;
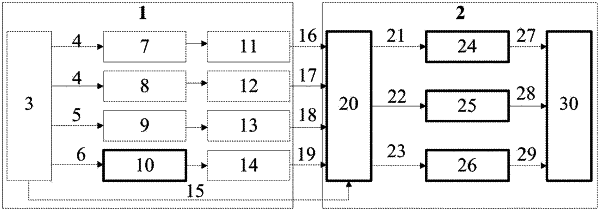
establishing, based on the traffic participant information, a position graph, a velocity graph, an acceleration graph, and a class graph, into each of which expert experience is introduced;
capturing topological structure relationships and time dependence relationships from the position graph, the velocity graph, the acceleration graph, and the class graph based on four parallel spatial relationship capture networks and time dependence relationship capture networks, to obtain a position hidden state, a velocity hidden state, an acceleration hidden state, and a class hidden state;
classifying the position hidden state, the velocity hidden state, the acceleration hidden state, and the class hidden state through determination by equations based on the serial numbers to obtain a hidden state set of traffic participants; and
decoding hidden states of the traffic participants separately using a multi-mode decoder based on traffic participant classes to obtain future trajectory predictions of the traffic participants;
planning trajectory for an intelligent vehicle based on the future trajectory predictions of the traffic participants.
|