| CPC G06V 10/44 (2022.01) [G06F 18/214 (2023.01); G06F 18/23 (2023.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06V 10/60 (2022.01); G06V 10/764 (2022.01); G06V 10/774 (2022.01); G06V 10/82 (2022.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
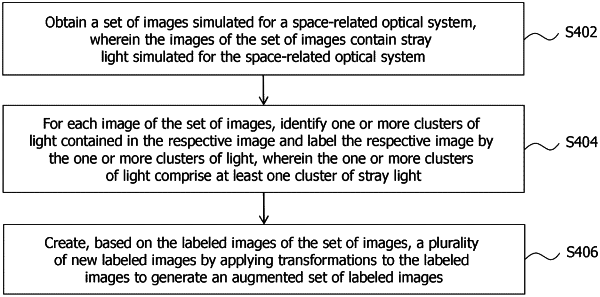
1. A method for generating a labeled set of images for use in machine learning based stray light characterization for space-related optical systems, the method comprising:
(a) obtaining a set of images simulated for a space-related optical system, wherein the images of the set of images contain stray light simulated for the space-related optical system;
(b) for each image of the set of images,
identifying one or more clusters of light contained in a respective image, wherein the one or more clusters of light are identified using an unsupervised machine learning algorithm, and
labeling the respective image by the one or more clusters of light, wherein the respective image is labeled pixel-wise, wherein each pixel of the respective image is assigned at least one label indicating to which of the one or more clusters of light the pixel belongs, wherein the one or more clusters of light comprise a cluster of nominal light, which is the most bright cluster of light contained in the respective image, wherein the one or more clusters of light further comprise at least one cluster of stray light, wherein each of the at least one cluster of stray light identified in the respective image is representative of a different shape of stray light contained in the respective image; and
(c) creating, based on the labeled images of the set of images, a plurality of new labeled images by applying mathematical image transformations to the labeled images to generate an augmented set of labeled images, wherein the transformations comprise at least one of rotation, translation, scaling, amplitude adjustment or any other type of image transformation which creates variance in the newly created labeled images, and wherein at least one of the transformations applied to the labeled images is performed cluster-wise, such that each transformation is performed on one of the one or more clusters of light independently from the transformations performed on others of the one or more clusters of light, so that, for each cluster, a different transformation may be applied.
|