| CPC G06T 7/80 (2017.01) [B60W 50/14 (2013.01); B60W 60/001 (2020.02); G01S 7/497 (2013.01); H04N 17/002 (2013.01); H04N 23/695 (2023.01); B60W 2050/146 (2013.01); B60W 2420/403 (2013.01); B60W 2420/408 (2024.01); G06T 2207/10028 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30244 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30252 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
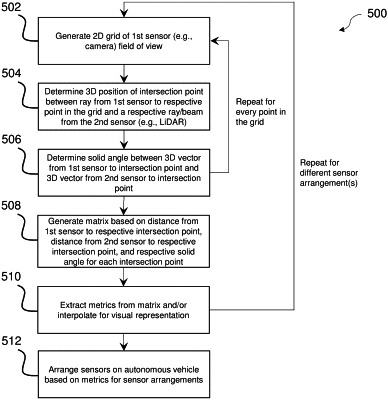
1. A method for parallax estimation for sensors for autonomous vehicles performed by a parallax estimation and sensor placement system, comprising:
generating a two-dimensional grid based on a field of view of a first sensor of an autonomous vehicle, the grid comprising a plurality of points;
for each respective point of the plurality of points, determining a three-dimensional position of a respective intersection point between a first respective ray from the first sensor to the respective point of the plurality of points and a second respective ray from a second sensor of the autonomous vehicle, wherein a plurality of intersection points comprises each respective intersection point for each respective point of the plurality of points;
for each respective intersection point of the plurality of intersection points, determining a respective solid angle based on a first three-dimensional vector from the first sensor to the three-dimensional position of the respective intersection point and a second three-dimensional vector from the second sensor to the three-dimensional position of the respective intersection point;
generating a matrix based on a first distance from the first sensor to each respective intersection point, a second distance from the second sensor to each respective intersection point, and the solid angle for each respective intersection point;
extracting at least one metric from the matrix;
adjusting an arrangement of the first sensor and the second sensor based on the at least one metric; interpolating the two-dimensional grid based on the at least one metric; and
displaying a visual representation based on interpolating the two-dimensional grid, wherein displaying the visual representation comprises displaying a gradient of at least one of shades or colors based on the at least one metric across a two-dimensional image.
|