| CPC G06T 7/0002 (2013.01) [G06N 3/08 (2013.01); G06T 3/40 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20076 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20084 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30168 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
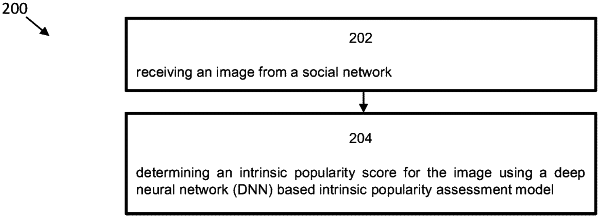
1. A method of content compression, the method comprising:
compressing information with a variable compression rate corresponding to an intrinsic popularity score of a content of the information, wherein the content of the information comprises an image; and
before the information is compressed, determining the intrinsic popularity score of the image using a deep neural network (DNN) based intrinsic popularity assessment model;
wherein the compressing of the information comprises:
classifying the intrinsic popularity score into a popularity level; and
compressing the image with the variable compression rate, the variable compression rate corresponding to the popularity level, the variable compression rate being in a negative correlation to the corresponding intrinsic popularity score, wherein the image is compressed by using a DNN based autoencoder, the DNN based autoencoder comprising learnable weights, the learnable weights being learnt according to an objective function
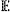 given by given by 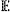 = =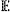 r+λ r+λ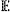 d, where d, where 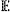 r is a coding cost, r is a coding cost, 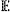 d is a reconstruction error, and λ is a Lagrange multiplier for controlling rate-distortion trade-off, and wherein A is a monotonic increasing function of the popularity level such that more bits are allocated for more popular images to thereby enable the image to be compressed with the variable compression rate corresponding to the popularity level and in the negative correlation to the corresponding intrinsic popularity score. d is a reconstruction error, and λ is a Lagrange multiplier for controlling rate-distortion trade-off, and wherein A is a monotonic increasing function of the popularity level such that more bits are allocated for more popular images to thereby enable the image to be compressed with the variable compression rate corresponding to the popularity level and in the negative correlation to the corresponding intrinsic popularity score. |