| CPC G06N 3/08 (2013.01) [G06N 3/063 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A device, comprising:
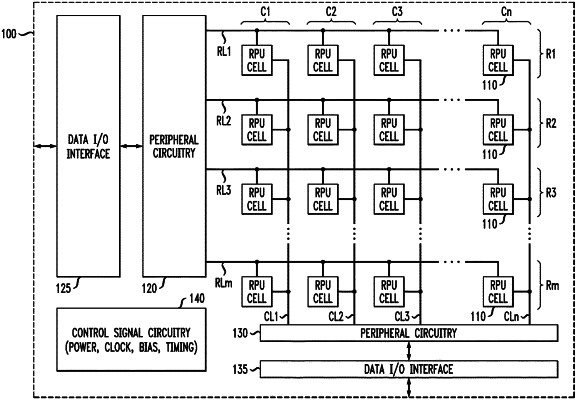
an array of resistive processing unit (RPU) cells;
first control lines extending in a first direction across the array of RPU cells, and second control lines extending in a second direction across the array of RPU cells, wherein each RPU cell is connected at an intersection of one of the first control lines and one of the second control lines;
peripheral circuitry coupled to the first control lines and to the second control lines, wherein the peripheral circuitry comprises readout circuitry which is shared by the first control lines and the second control lines; and
a control system operatively coupled to the peripheral circuitry, wherein the control system generates control signals to control the peripheral circuitry to perform a first operation on the array of RPU cells and to perform a second operation on the array of RPU cells;
wherein the control signals comprise:
a first configuration control signal to configure the readout circuitry to have a first hardware configuration when the first operation is performed on the array of RPU cells, to enable readout of signals in a first output signal range; and
a second configuration control signal to configure the readout circuitry to have a second hardware configuration, which is different from the first hardware configuration, when the second operation is performed on the array of RPU cells, to enable readout of signals in a second output signal range, which is smaller than the first output signal range.
|