| CPC G06F 3/0659 (2013.01) [G06F 3/0611 (2013.01); G06F 3/0679 (2013.01); G11C 16/10 (2013.01); G11C 16/26 (2013.01); G11C 16/0483 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
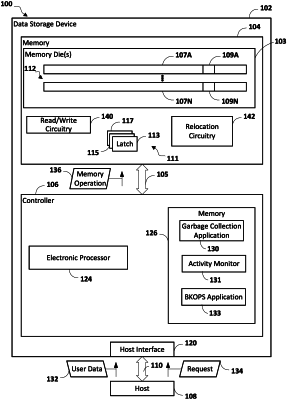
1. A data storage device, comprising:
a non-volatile memory device including a plurality of memory blocks, the memory blocks including a plurality of memory dies; and
a controller coupled to the non-volatile memory device and configured to:
receive a read command from an external device,
determine whether a read operation associated with the read command is a sequential read operation, and
in response to determining that the read operation is the sequential read operation, executing one or more relocation operations, wherein the one or more relocation operations are executed in an order based on a priority order associated with each of the one or more relocation operations,
wherein the priority is based on a type of relocation operation associated with the each of the one or more relocation operations,
wherein the one or more relocation operations comprise one or more of a Quad Level Cell (“QLC”)-QLC compaction operation type, a Single Level Cell (“SLC”)-SLC compaction operation type, and an SLC-QLC folding operation type, and
wherein the QLC-QLC compaction operation type has a higher priority order than the SLC-SLC compaction operation type and the SLC-QLC folding operation type.
|