| CPC G06F 3/0611 (2013.01) [G06F 3/0604 (2013.01); G06F 3/0644 (2013.01); G06F 3/0659 (2013.01); G06F 3/067 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
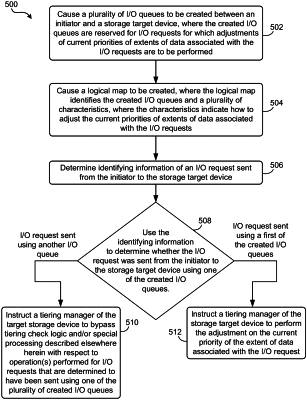
1. A computer-implemented method, comprising:
causing a plurality of nonvolatile memory express (NVMe) I/O queues to be created between an initiator and a storage target device,
wherein a first subset of the created I/O queues are priority adjustment I/O queues that are reserved for I/O requests for which adjustments of current priorities of extents of data associated with the I/O requests are to be performed,
wherein the adjustments are based on anticipated demand(s) and/or anticipated lack of demand(s), in a predetermined future period of time, for the extents of data associated with the I/O requests,
wherein a second subset of the created I/O queues are used for I/O requests for regular I/O operations, the I/O queues in the second subset being different than the I/O queues in the first subset;
determining identifying information of an I/O request sent from the initiator to the storage target device,
wherein the I/O request is sent from the initiator to the storage target device using an in-band protocol command in which direct communication occurs between the initiator and the storage target device;
determining, using the identifying information, whether the I/O request was sent from the initiator to the storage target device using only one of the created priority adjustment I/O queues and none of the other created I/O queues; and
in response to a determination that the I/O request was sent from the initiator to the storage target device using only a first of the created priority adjustment I/O queues and none of the other created I/O queues, having one of the adjustments associated therewith, instructing a tiering manager of the storage target device to perform the adjustment on the current priority of the extent of data associated with the I/O request,
wherein the instruction to the tiering manager specifies a numerical multiplier to apply to a current heat extent of the current priority of the extent of data.
|