| CPC G01R 33/5608 (2013.01) [G01R 33/445 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
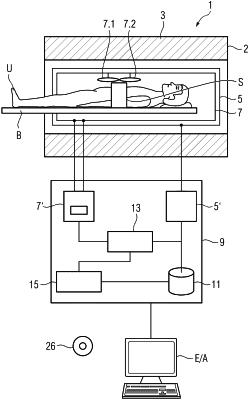
1. A computer-implemented magnetic resonance image optimisation method, comprising:
mapping an image of an object obtained using a static magnetic field and an incident radio frequency signal by dividing the image into identically sized three-dimensional voxels, dimensions of the identically sized three-dimensional voxels being determined by a desired mapping resolution;
representing each voxel in a Euclidean n-dimensional space, where n≥3, each voxel having a voxel location represented by at least a two-dimensional position and at least one voxel characteristic represented by at least one further dimension;
clustering the Euclidean n-dimensional space by grouping together voxels having similar voxel characteristics to create homogenous clusters;
determining a centre or centroid of each cluster;
using either the determined centre or centroid of each cluster, or the voxel closest to the determined centre or centroid, as a super-voxel in an optimisation procedure; and
generating an optimised diagnostic image of the object,
wherein each voxel characteristic includes at least one of a local transmit magnetic field amplitude induced by the incident RF signal at the voxel location or a local static magnetic field amplitude at a respective voxel location.
|