| CPC G01N 33/54373 (2013.01) [G01N 27/4145 (2013.01); G01N 27/4146 (2013.01); G01N 33/5432 (2013.01)] | 22 Claims |
|
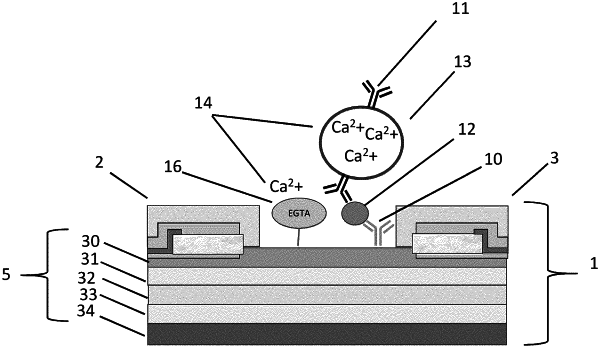
1. A method for the detection of a target marker in a solution including charged ions and unrelated ions comprising:
providing a liposome in solution containing metal ions, the liposome including a detection antibody configured to bind a target marker;
providing a field-effect transistor with a source-drain channel comprising a surface functionalized with both a capture antibody to selectively bind to the target marker and a metal ion chelator or metal ion derivatized chelator;
selectively binding the target marker to the detection antibody included with the liposome;
selectively binding the target marker to the capture antibody to dispose the target marker and bound liposome to the source-drain channel of the field-effect transistor;
releasing the metal ions from the liposome;
selectively binding the metal ion chelator or metal ion derivatized chelator disposed on the functionalized surface of the source-drain channel with the metal ions released from the liposome; and
causing a change in current in the field-effect transistor as a result of the selective binding of the metal ion chelator or metal ion derivatized chelator with the metal ions released from the liposome without interference of the detection of the metal ions by screening oppositely charged ions and unrelated ions in the solution; and
wherein the change in current is indicative of detection of the target marker.
|