| CPC C12Q 1/6869 (2013.01) [G16B 20/50 (2019.02); G16B 30/10 (2019.02)] | 11 Claims |
|
1. A method for analyzing cleavage and/or repair events for a site specific nuclease, the method comprising:
(a) contacting a cell or tissue with the site specific nuclease, wherein contacting the cell or tissue with the site specific nuclease results in cleavage and/or repair of genomic DNA in the cell or tissue;
(b) obtaining a genomic DNA sample from the cell or tissue that has been contacted with the site specific nuclease;
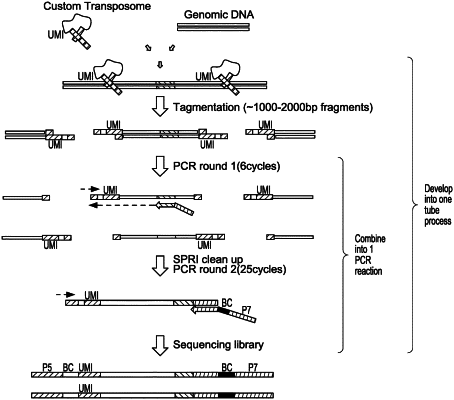
(c) contacting the genomic DNA sample with a transposase and a transposon comprising a first detection sequence at the 5′ end of the transposon, under conditions whereby the transposon is inserted into the genomic DNA sample and the genomic DNA sample is fragmented into a plurality of tagmented double-stranded nucleic acid fragments comprising the transposon attached to the 5′ end of the nucleic acid fragments;
(d) amplifying the tagmented nucleic acid fragments using
(i) a first fixed primer comprising a nucleotide sequence complementary to a predetermined location in the genomic DNA and comprising a second detection sequence at its 5′ end, and
(ii) a second selective primer comprising a nucleotide sequence complementary to at least a portion of the first detection sequence,
to form amplified nucleic acid fragments comprising the first detection sequence, the transposon attached to the 5′ end of the nucleic acid fragments, and the second detection sequence;
(e) sequencing the amplified nucleic acid fragments to generate sequencing data; and
(f) analyzing the sequencing data for the cleavage and/or repair events of the site specific nuclease.
|