| CPC C12N 5/0629 (2013.01) [A61K 48/0058 (2013.01); A61K 48/0075 (2013.01); A61K 48/0091 (2013.01); C12N 2510/00 (2013.01); C12N 2760/16043 (2013.01)] | 23 Claims |
|
1. A method for treating Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (RDEB) in a human patient having one or more mutations in both copies of a human collagen VII A1 (Col7A1) gene and suffering from RDEB, the method comprising:
(a) subjecting the human patient to one or more tests selected from replication competent retrovirus (RCR), COL7A1-sensitive cytotoxic T-cells, or a combination thereof;
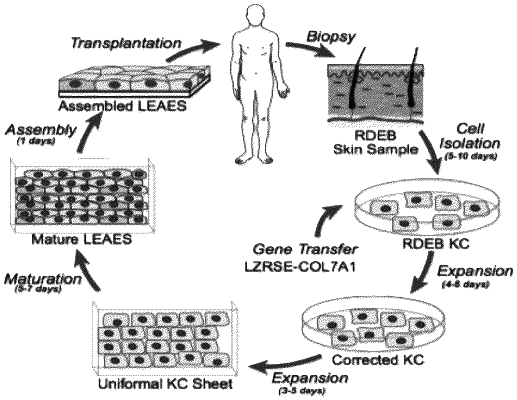
(b) obtaining from the human patient a population of skin cells comprising keratinocytes;
(c) isolating a population of keratinocytes comprising the one or more mutations in the col7A1 gene from the population of skin cells, and culturing the isolated population of keratinocytes on a collagen 1 peptide in a first keratinocyte culture medium;
(d) transducing the isolated population of keratinocytes ex vivo with a retroviral vector comprising a promoter operably linked to a genetic construct encoding a functional human collagen VII (COL7A1) protein to generate genetically corrected keratinocytes that meet pre-release criteria for viral transduction efficiency (VTE) >50% and proviral genome copy number (PGCN) of less than or equal to 1.5;
(e) culturing the genetically corrected keratinocytes in the first keratinocyte culture medium to form an autologous COL7A1 corrected keratinocyte sheet;
(f) subjecting the autologous COL7A1 corrected keratinocyte sheet to one or more pre-release tests selected from a group consisting of VTE test, PGCN test, and replication competent retrovirus (RCR) test;
(g) maturing the autologous COL7A1 corrected keratinocyte sheet to form engineered autologous epidermal sheets, wherein maturing comprises culturing the autologous COL7A1 corrected keratinocyte sheet in a second culture medium; and wherein the second culture medium comprises DFF31 medium;
(h) assembling the engineered autologous epidermal sheets; and
(i) transplanting a graft of the assembled engineered autologous epidermal sheets to an RDEB-induced wound of the human patient.
|