| CPC B61L 15/0081 (2013.01) [B61L 15/0072 (2013.01); B61L 15/009 (2013.01); G06F 3/14 (2013.01); B60W 2050/146 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
1. An information processing apparatus, comprising:
processing circuitry configured to detect a state of a device by applying device information on the device to a state detection model generated based on past device information on the device and characteristic information indicating characteristics of a moving body equipped with the device,
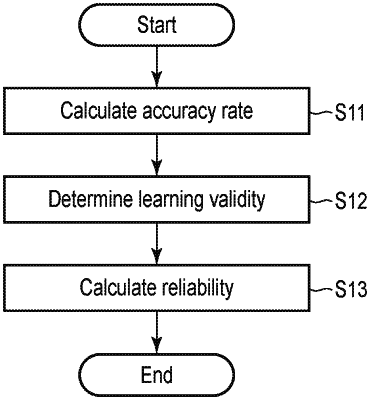
wherein the processing circuitry is further configured to select the state detection model from a plurality of state detection models, based on a calculated reliability of each of the plurality of state detection models, the reliability being calculated, for each model of the plurality of state detection models, by
(1) determining a first value indicating a number of times for which the model output a value indicating a failure of the device that occurred during a predetermined past time period,
(2) determining a second value indicating a number of actual failures that occurred for the device in the predetermined past time period,
(3) determining an accuracy by multiplying a state change amount by the determined first value and dividing by the determined second value,
(4) determining a learning validity value, which is zero when a failure case occurred during a training period of the model and is one when the failure case did not occur during the training period, and
(5) determining the reliability by multiplying the determined accuracy by the determined learning validity value.
|