| CPC B60W 40/13 (2013.01) [B60W 40/112 (2013.01); B60W 2300/14 (2013.01); B60W 2420/403 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method of measuring how level a trailer is, wherein the trailer is connected to a vehicle, the method comprising:
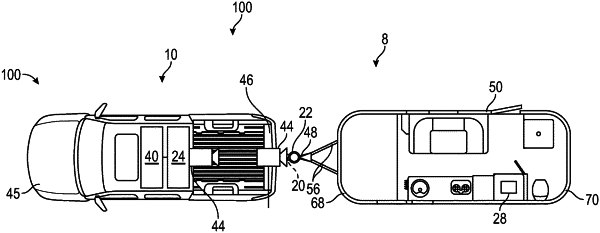
capturing an image of the trailer using a rear facing camera of the vehicle, the image encompassing a front face of the trailer;
receiving, via at least one processor, a vehicle levelness parameter from a vehicle levelness estimator of the vehicle, the vehicle levelness parameter indicating how level the vehicle is, based on a digital elevation map and a current location of the vehicle;
determining, via the at least one processor, a rotation angle of the trailer relative to the vehicle based on the image and a comparison of the image with a stored reference image that was captured at a known roll angle of the trailer;
determining, via the at least one processor, a vision-based estimated trailer levelness parameter based on the rotation angle and the vehicle levelness parameter, the vision-based estimated trailer levelness parameter indicating how level the trailer is using the image from the rear facing camera of the vehicle, the vehicle level parameter from the digital elevation map and the current location of the vehicle, and the stored reference image;
receiving, via the at least one processor, a sensor-based trailer levelness parameter based on a levelness measurement from a trailer levelness estimator disposed on the trailer, wherein the levelness estimator comprises an inertial measurement unit (IMU) that is disposed on a surface of the trailer;
determining, via the at least one processor, a fused trailer levelness parameter based on a fusion of both (A) the vision-based estimated trailer levelness parameter with (B) the sensor-based trailer levelness parameter, utilizing different estimates at different respective times of both the vision-based estimated trailer levelness parameter and the sensor-based trailer levelness parameter, wherein the fusion of the estimated trailer levelness parameter with the sensor based trailer levelness parameter is weighted based on an inverse of variance that is tracked over time;
outputting, via the at least one processor, the estimated trailer levelness parameter; and
automatically adjusting a height under one or more wheels of the trailer, in accordance with instructions provided by the at least one processor.
|