| CPC B60T 8/17551 (2013.01) [B60T 8/17552 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
1. A path tracking control method for an intelligent electric vehicle, comprising:
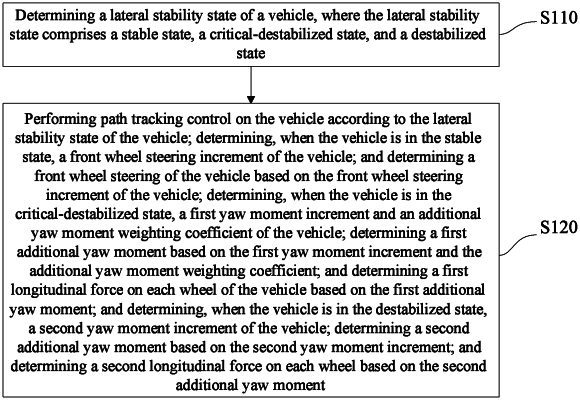
determining a lateral stability state of a vehicle, wherein the lateral stability state comprises a stable state, a critical-destabilized state, and a destabilized state;
performing path tracking control on the vehicle according to the lateral stability state of the vehicle;
determining, when the vehicle is in the stable state, a front wheel steering increment of the vehicle; and determining a front wheel steering of the vehicle based on the front wheel steering increment of the vehicle;
determining, when the vehicle is in the critical-destabilized state, a first yaw moment increment and an additional yaw moment weighting coefficient of the vehicle; determining a first additional yaw moment based on the first yaw moment increment and the additional yaw moment weighting coefficient; and determining a first longitudinal force on each wheel of the vehicle based on the first additional yaw moment; and
determining, when the vehicle is in the destabilized state, a second yaw moment increment of the vehicle; determining a second additional yaw moment based on the second yaw moment increment; and determining a second longitudinal force on each wheel based on the second additional yaw moment;
wherein the stable state is determined by
 the critical-destabilized state is determined by
 and
the destabilized state is determined by
 wherein β represents a center-of-mass sideslip angle of the vehicle; β represents a center-of-mass sideslip angular velocity; k represents a slope; c is constant; and μ represents a road surface adhesion coefficient.
|