| CPC B21B 1/20 (2013.01) [B21B 27/025 (2013.01)] | 5 Claims |
|
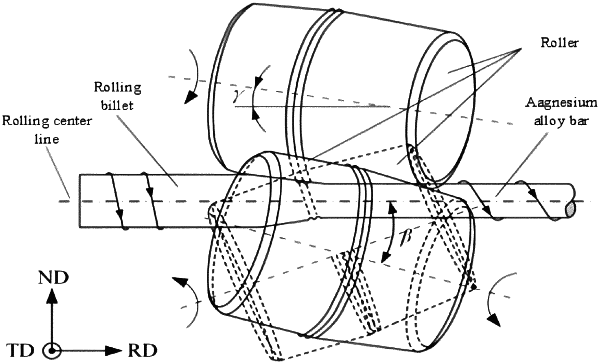
1. A corrugated skew rolling preparation method of a magnesium alloy bar with a gradient structure, adopts a three-roller skew rolling mill, wherein, adding a corrugated curve to a flat roll rolling section of the three-roller skew rolling mill to form a corrugated roll, the billet used is as-cast magnesium alloy bar, and steps of the preparation method are as follows:
S1, simulated rolling physical experiment: adopting an Abaqus finite element software to carry out a simulation calculation to obtain a macroscopic deformation law of the as-cast magnesium alloy bar and carry out a rolling physical experiment;
S2, rolling parameters setting: according to results of the rolling physical experiment in S1, setting rolling parameters of a transformed three-roller skew rolling mill, wherein a roll feed angle γ is set to 8° to 12°, a rolling angle β is set to 6° to 10°, a roll speed is set to 300 r/min to 500 r/min, and a throat diameter is adjusted to 60 mm;
S3, bar homogenization annealing treatment: in an argon environment, adopting a box furnace to homogenize and anneal the as-cast magnesium alloy bar, a homogenized annealing temperature is 520° C. to 540° C., and a annealing holding time is 50 minutes to 70 minutes;
S4, heating treatment of bars before rolling: in the argon environment, adopting the box furnace to heat an annealed magnesium alloy bar after S3 treatment to 350° C. to 400° C., and keeping 20 minutes to 30 minutes;
S5, three-roller skew mill rolling: sending the annealed magnesium alloy bar treated by S4 to the three-roller skew rolling mill for rolling, to obtain rolled parts;
S6, cooling of the rolled parts after rolling: adopting an air cooling method to cool the rolled parts, to obtain a target magnesium alloy bar with a gradient structure;
wherein, in S1, the simulated rolling physical experiment comprises the following steps:
S1.1, establishing a finite element model: in the Abaqus finite element software, replacing all three rolling flat rolls in the flat roll rolling section of the three-roller skew rolling mill with corrugated rolls, wherein the corrugated curves on the corrugated rolls are sinusoidal curves, and the three corrugated rolls are equidistant interval distributed around a rolling center line, wherein the roll feed angle γ is 8° to 12°, the rolling angle β is 6° to 10°;
S1.2, simulated rolling: a rolling billet is the annealed magnesium alloy bar, inputting the rolling parameters, which are obtained from thermal simulation compression, into the Abaqus finite element software, defining a contact type between the corrugated roll and the annealed magnesium alloy bar as a rigid-flexible contact, setting an initial rolling temperature at 350° C. to 400° C., setting the roll speed at 300 r/min to 500 r/min, setting a bar feed speed at 10 mm/s to 15 mm/s and a roll temperature is room temperature, and the bar mesh is divided into mesh cells, adopting a thermodynamic coupling explicit dynamic analysis to simulate the finite element model;
S1.3, rolling parameters extraction: selecting three tracking points from the center to the surface of the magnesium alloy bar after the step of S1.2 simulated rolling, and a r/R of the three tracking points are 0.1, 0.5 and 0.9 respectively, wherein R represents the radius of the magnesium alloy bar after the step of S1.2 simulated rolling and r represents the distance between the tracking points and the rolling center line; extracting values of equivalent plastic strain, temperature values, values of shear stress and values of shear strain of the three tracking points to obtain an evolution law of the magnesium alloy bar during a process of corrugated rolls rolling;
S1.4, orthogonal experiment: to ensure that other rolling parameters remain unchanged, by setting the corrugated roll and flat roll respectively to simulate the orthogonal experiment; and comparing the distribution difference of the values of equivalent plastic strain, the temperature values, the values of shear stress and the values of the shear strain of the as-cast magnesium alloy bar during the process of corrugated roll rolling and flat roll rolling, respectively.
|