| CPC A61M 16/026 (2017.08) [A61B 5/0816 (2013.01); A61B 5/14551 (2013.01); A61M 2202/0007 (2013.01); A61M 2202/0208 (2013.01); A61M 2205/18 (2013.01); A61M 2230/42 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
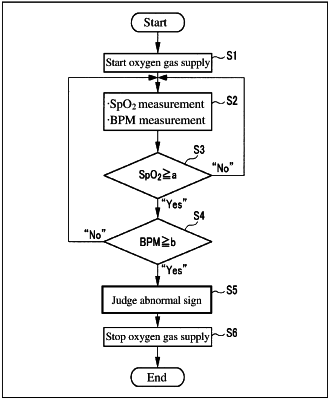
1. An oxygen supply device supplying a user with an oxygen gas for inhalation, comprising:
a first sensor unit configured to sense information on percutaneous arterial oxygen saturation (SpO2) of the user,
a second sensor unit configured to sense information on vital signs that fluctuate in accordance with a rise in carbon dioxide concentration in blood of the user, the information on vital signs indicating a respiratory frequency, in breaths per minute (BPM), of the user,
a control unit configured to control a supply rate of the oxygen gas, and, under the controlled supply rate, judging a risk of an abnormal increase in the carbon dioxide partial pressure in arterial blood of the user,
wherein the control unit is further configured to:
control a supply of the oxygen gas;
check and determine whether the level of percutaneous arterial oxygen saturation is equal to or larger than a first threshold;
in response to determining that the level of percutaneous arterial oxygen saturation is equal to or larger than the first threshold, check and determine whether the information on the vital signs is out of a predetermined range;
in response to determining that the information on the vital signs is out of the predetermined range, judge the level of percutaneous arterial oxygen saturation and the information on the vital signs as indicating a sign of the abnormal increase in the carbon dioxide partial pressure in arterial blood of the use; and
control the supply of the oxygen gas based on whether the level of percutaneous arterial oxygen saturation and the information on the vital signs is judged as indicating the sign of the abnormal increase in the carbon dioxide partial pressure in arterial blood of the user.
|