| CPC A61K 31/47 (2013.01) [A61K 45/06 (2013.01); A61P 35/00 (2018.01); C07D 215/233 (2013.01)] | 34 Claims |
|
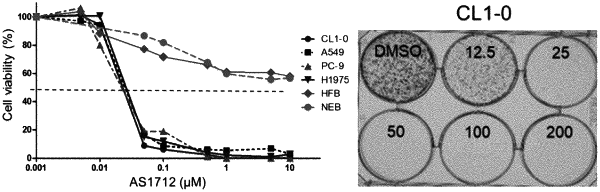
1. A method of treating one or more cancers of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, colon cancer, head cancer, neck cancer, and head and neck cancer in a subject in need thereof, the method comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I):
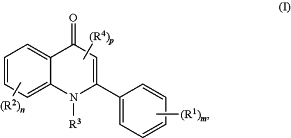 or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, co-crystal, tautomer, or stereoisomer thereof, wherein:
each instance of R1 is independently halogen, —C(═O)(unsubstituted alkyl), unsubstituted or substituted alkyl by halogen, unsubstituted or substituted alkenyl by halogen, unsubstituted or substituted alkynyl by halogen, unsubstituted or substituted carbocyclyl by halogen, unsubstituted heterocyclyl, unsubstituted aryl, unsubstituted heteroaryl, —CN, —ORD1, —N(RD1a)2, or —SRD1;
each instance of R2 is independently halogen, —C(═O)Raa, —CHO, —CO2Raa, —C(═O)N(Rbb)2, —C(═O)(OCH2CH2)zOR2c, —(CH2)xORaa, —C(═S)N(Rbb)2, —C(═O)SRaa, —C(═S)SRaa, —C(═NRbb)Raa, —C(═NRbb)ORaa, —C(═NRbb)N(Rbb)2, —C(═O)NRbbSO2Raa, unsubstituted alkyl, unsubstituted alkenyl, unsubstituted alkynyl, unsubstituted carbocyclyl, unsubstituted heterocyclyl, unsubstituted aryl, unsubstituted heteroaryl, —CN, —ORD1, —N(RD1a)2, or —SRD1; and at least one R2 is —C(═O)Raa, —CHO, —CO2Raa, —C(═O)N(Rbb)2, —C(═O)(OCH2CH2)zOR2c, —(CH2)xORaa, —C(═S)N(Rbb)2, —C(═O)SRaa, —C(═S)SRaa, —C(═NRbb)Raa, —C(═NRbb)ORaa, —C(═NRbb)N(Rbb)2, —C(═O)NRbbSO2Raa or —CN;
R3 is hydrogen, unsubstituted alkyl, or a nitrogen protecting group;
each instance of R4 is independently halogen, —C(═O)Raa, —CHO, —CO2Raa, —C(═O)N(Rbb)2, —C(═NRbb)Raa, —C(═NRbb)ORaa, —C(═NRbb)N(Rbb)2, —C(═O)NRbbSO2Raa, —C(═S)N(Rbb)2, —C(═O)SRaa, —C(═S)SRaa, unsubstituted alkyl, unsubstituted alkenyl, unsubstituted alkynyl, unsubstituted carbocyclyl, unsubstituted heterocyclyl, unsubstituted aryl, unsubstituted heteroaryl, —CN, —ORD1, —N(RD1a)2, or —SRD1;
RD1 is hydrogen, —C(═O)Raa, —CHO, —CO2Raa, —C(═O)N(Rbb)2, —C(═NRbb)Raa, —C(═NRbb)ORaa, —C(═NRbb)N(Rbb)2, —C(═O)NRbbSO2Raa, —C(═S)N(Rbb)2, —C(═O)SRaa, —C(═S)SRaa, unsubstituted alkyl, unsubstituted alkenyl, unsubstituted alkynyl, unsubstituted carbocyclyl, unsubstituted heterocyclyl, unsubstituted aryl, unsubstituted heteroaryl, an oxygen protecting group when attached to an oxygen atom, or a sulfur protecting group when attached to a sulfur atom;
each occurrence of RD1a is hydrogen, —C(═O)Raa—CHO, —CO2Raa, —C(═O)N(Rbb)2, —C(═NRbb)Raa, —C(═NRbb)ORaa, —C(═NRbb)N(Rbb)2, —C(═O)NRbbSO2Raa, —C(═S)N(Rbb)2, —C(═O)SRaa, —C(═S)SRaa, unsubstituted alkyl, unsubstituted alkenyl, unsubstituted alkynyl, unsubstituted carbocyclyl, unsubstituted heterocyclyl, unsubstituted aryl, unsubstituted heteroaryl, or a nitrogen protecting group; or optionally-two instances of RD1a are taken together with their intervening atoms to form an unsubstituted heterocyclic or unsubstituted heteroaryl ring;
Raa is hydrogen, unsubstituted alkyl, unsubstituted alkenyl, unsubstituted alkynyl, unsubstituted carbocyclyl, unsubstituted heterocyclyl, unsubstituted aryl, unsubstituted heteroaryl, or an oxygen protecting group when attached to an oxygen atom;
each occurrence of Rbb is hydrogen, unsubstituted alkyl, unsubstituted alkenyl, unsubstituted alkynyl, unsubstituted carbocyclyl, unsubstituted heterocyclyl, unsubstituted aryl, unsubstituted heteroaryl, or a nitrogen protecting group when attached to a nitrogen atom;
R2c is hydrogen;
m is 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5;
n is 1, 2, 3, or 4;
x is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6;
z is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6; and
p is 0 or 1.
|