| CPC A61B 5/163 (2017.08) [G06F 3/013 (2013.01); G06V 40/18 (2022.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method for predicting whether a user has a target health condition using eye images, the method comprising:
providing automated guidance to the user to obtain, using a computing device operated by the user, a plurality of images including the user's sclera, each of the images corresponding to a guided direction of the user's gaze;
receiving the images from the computing device by way of a network;
verifying that the images sufficiently show the user's sclera, including by estimating a direction of the user's gaze and confirming that the estimated direction for a given one of the images conforms with the guided direction corresponding to that image;
generating feature-enhanced image data by:
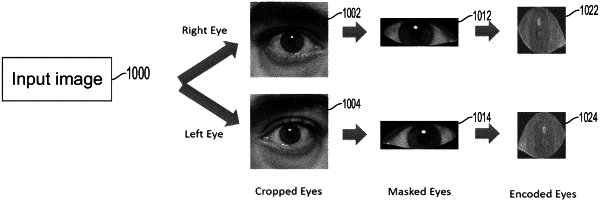
extracting an eye image of the user from at least one image from the plurality of images;
masking an iris area of the extracted eye image of the user in the at least one image such that the iris area of the extracted eye image is absent from downstream processing; and
applying an autoencoder to enhance features corresponding to the user's sclera in the at least one image to generate the feature-enhanced image data; and
computing a prediction of whether the user has the target health condition by providing the feature-enhanced image data to a convolutional neural network (CNN), wherein the feature-enhanced image data comprises image data representing ocular manifestations in the user's sclera and outside of the masked iris area in the extracted eye image in the at least one image, wherein the target health condition is related to coronavirus, and the CNN comprises a plurality of layers including a convolutional layer, an non-linear activation layer and a max-pooling layer.
|