| CPC A61B 5/0295 (2013.01) [A61B 5/02416 (2013.01); A61B 5/0261 (2013.01); A61B 5/14551 (2013.01); A61B 5/4848 (2013.01); A61B 5/7278 (2013.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
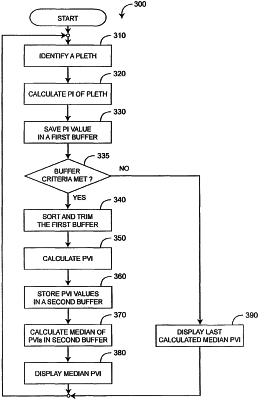
1. A computerized plethysmograph variability method using a signal processor comprising:
receiving a data signal from a physiological sensor coupled to a patient;
generating a plethysmograph waveform based at least in part on the data signal, wherein the plethysmograph waveform comprises a plurality of pulses corresponding to pulsatile blood flow within tissue of the patient;
accumulating, in a first buffer, a plurality of perfusion values corresponding to the plurality of pulses, the plurality of perfusion values derived based on the plurality of pulses;
determining if a sufficient amount of physiologically acceptable data is in the first buffer based at least on a length of a respiration cycle of the patient, wherein the signal processor is configured to perform specific operations when there is sufficient amount of data and when there is insufficient amount of data in the first buffer over time;
in response to determining that sufficient amount of data is in the first buffer for a specific period of time:
determining a plurality of variability values each indicative of variability of a series of the plurality of perfusion values;
calculating a plethysmograph variability index representative of the plurality of variability values; and
displaying the calculated plethysmograph variability index; and
in response to determining that insufficient amount of data is in the first buffer for the specific period of time:
displaying a previously calculated plethysmograph variability index stored in the signal processor.
|