| CPC A61B 34/20 (2016.02) [A61B 6/12 (2013.01); A61B 90/37 (2016.02); A61B 2034/102 (2016.02); A61B 2034/107 (2016.02); A61B 2034/2065 (2016.02); A61B 2090/376 (2016.02)] | 19 Claims |
|
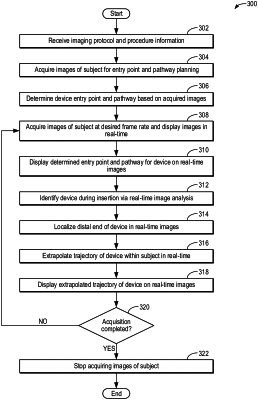
1. A method for an interventional imaging procedure, comprising:
identifying a medical device during insertion of the medical device within a subject based on live images of the insertion;
extrapolating a trajectory of the medical device during the insertion in real-time based on the live images of the insertion, wherein extrapolating the trajectory of the medical device comprises extending a predetermined distance beyond a distal end, the predetermined distance selected according to a selected procedure to be consistent in scale with a magnification and acquired angle of the live images; and
displaying the extrapolated trajectory of the medical device on the live images.
|
|
19. A method for an interventional imaging procedure, comprising:
identifying a medical device during insertion of the medical device within a subject based on live images of the insertion;
extrapolating a trajectory of the medical device during the insertion in real-time based on the live images of the insertion, a geometric model, and a mechanical model, wherein the geometric model is based on an orientation of the medical device, and wherein the mechanical model is based on physical properties of the medical device and physical properties of a tissue the medical device is penetrating; and
displaying the extrapolated trajectory of the medical device on the live images of the insertion, wherein the orientation comprises both a position of a distal end of the medical device and an angle with respect to a reference, and wherein the reference is a determined pathway for the medical device that is separate from the extrapolated trajectory.
|