| CPC G16C 20/90 (2019.02) [H04L 9/0825 (2013.01); H04L 9/0866 (2013.01); H04L 9/3247 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
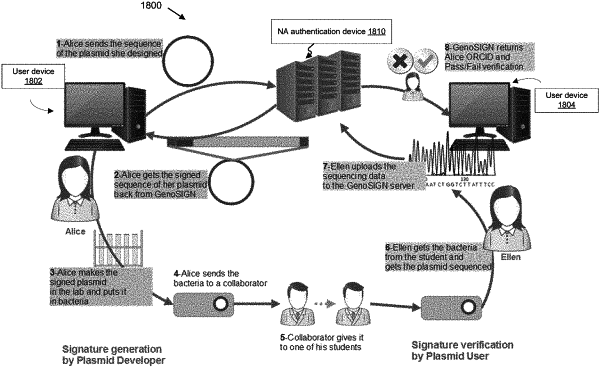
1. A processor-implemented nucleic acid crypto-signing method, comprising:
receiving a nucleic acid sequence from a user device associated with a user;
generating, via at least one processor, a first portion of a digital signature by encrypting a mapped value of the nucleic acid (NA) sequence using a private key associated with the user;
generating a second portion of the digital signature based on at least one of (1) a first unique identifier associated with the user, (2) a second unique identifier associated with the nucleic acid sequence, and (3) an error detection code;
identifying at least two insertion points in the nucleic acid sequence;
forming a completed digital signature by combining the first and second portions of the digital signature;
converting the completed digital signature into nucleic acid signature sequence data;
inserting the nucleic acid signature sequence between the at least two insertion points in the nucleic acid sequence to form a signed nucleic acid sequence; and
synthesizing the signed nucleic acid sequence using a synthesizer.
|